A Simple Definition of Metabolism, and How to Boost It

Men tend to burn more calories than women, even while resting. But metabolism is also affected by genetics, temperature, and some other factors.
5-Minute Crafts decided to find out what metabolism is, and how to boost it.
What is metabolism?
Metabolism is the ability of the body to convert calories into energy needed for the body’s normal functioning.
The name of this process is derived from the word which means “to change.” In ancient times, metabolism was compared to fire because scientists described this process as the transformation of food into heat.
The first recorded experiments were published in 1614. But the study of metabolism experienced the greatest development strides at the beginning of the 20th century.
How does it work?
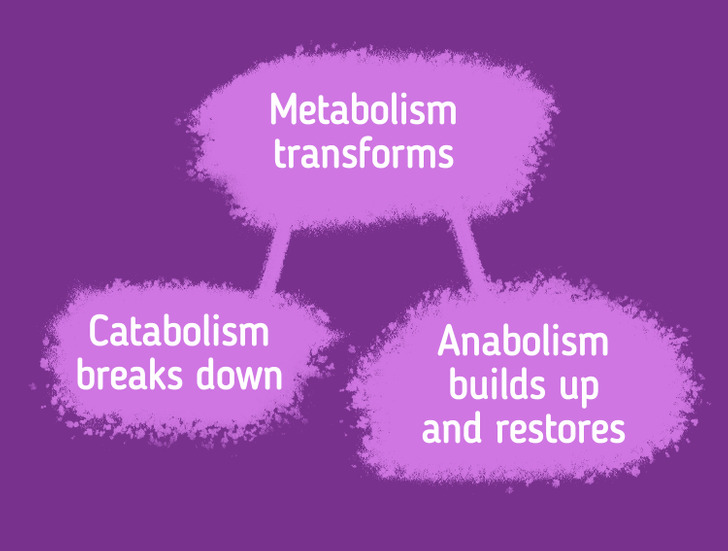
Briefly, the process of metabolism can be described as follows: calories from food, when combined with oxygen, release energy. The amount of energy that the body uses for its needs, like breathing, growing and repairing cells, circulating blood, and adjusting hormone levels, is the basal metabolic rate.
This ability of the body includes 2 more processes:
- catabolism is responsible for the breakdown of nutrients that come from food into simpler units
- anabolism is responsible for building up and restoring the body’s cells
Energy expenditure is continuous, but its rate can vary. For example, it’s usually lower in the morning.
What does the speed of metabolism depend on?

The metabolic rate of each person is unique and depends on several factors.
- Age. Usually, the amount of muscle tissue tends to decrease with age, while fat tissue tends to increase, so the process of burning calories slows down. For most people, metabolism steadily slows after age 40.
- Gender. Most often, men burn more calories than women of a similar age and weight, because the male body has less fat tissue and more muscle.
- Body composition. Usually, people who are larger tend to burn more calories even while resting. At the same time, muscle tissue burns more kilojoules than fat tissue.
- Physical activity. It may not necessarily be working out, but any movement, whether it’s walking to the store or fidgeting in a chair.
- Food digestion. The body uses energy to digest, absorb, and transport nutrients. The more often we eat, the more energy we use.
- Genetic predisposition. The metabolic rate partly depends on your genes.
- Environmental temperature. If it’s low, the body tends to spend more energy maintaining its temperature.
How to boost metabolism?

So, the metabolic rate often depends on genetic predisposition, gender, and age, and these factors can’t be controlled, as well as the amount of energy that is necessary for the functioning of all body systems. However, some tricks can still help boost metabolism.
- Physical activity. The more we move, the more energy is required. And the more intense the workout is, the longer the metabolic rate will remain high.
- Building muscle mass. Every pound of muscle burns about 6 calories, even at rest. Therefore, after strength training, the muscles of the whole body are activated and the average daily metabolic rate increases.
- Mandatory breakfast. Don’t skip your first meal of the day. A balanced breakfast containing protein and complex carbs will boost your energy levels and, with it, your metabolism.
- More water. Water is necessary to process calories, so it’s recommended to drink 1 glass of water before each meal. Also, you can snack on fruits or vegetables which contain a lot of water.
- Spicy food. Spicy food can temporarily boost your metabolism thanks to the natural chemicals it contains. Those who like to eat spicy food regularly may be able to notice a more lasting and noticeable effect.
- Eating more protein. The body spends much more energy on its absorption than on the digestion of carbs or fats. Therefore, it’s recommended to eat high-protein foods like turkey, fish, chicken, tofu, nuts, beans, eggs, and lean beef.
- No strict diets. They slow down the metabolic rate in order to conserve energy. Also when losing weight due to a calorie deficit, not only fat but also muscle mass can decrease.
- The number of meals. Small meals eaten every 3-4 hours can speed your metabolism, while large meals with long breaks in between, on the contrary, slow it down.
- Coffee. When consumed in moderation, this invigorating drink can also increase the metabolic rate, but only for a short time.
- Green tea. Thanks to the catechins it contains, this drink stimulates the body to burn more calories.
- Sleeping at least 7 hours. If you don’t get enough sleep or feel tired, your level of activity can decrease, and your metabolic rate with it.