All About Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are nutritional elements that come to our bodies with food and that turn into glucose during the process of digestion. Glucose, in its turn, gives energy to the body for performing its functions. Carbohydrates are there in various food products. The level of sugar in your blood and the timing around how long you will feel full depends on their type.
5-Minute Crafts wants to tell you what complex carbohydrates are, how different they are from simple carbohydrates, how many carbohydrates should be consumed with food, and what sources are “better” choices.
What types of carbohydrates are there
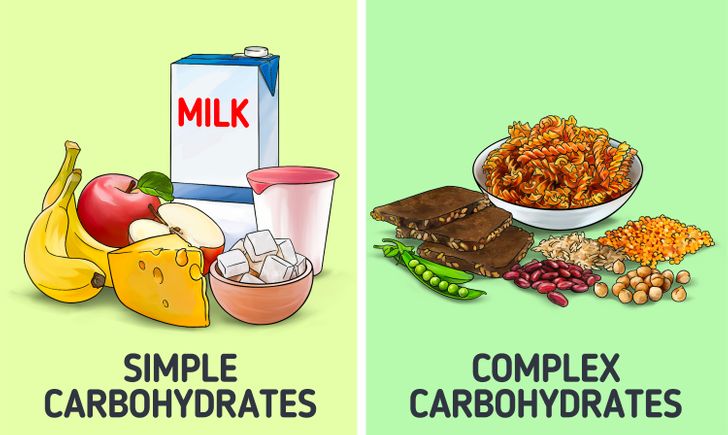
Carbohydrates can be simple and complex:
- Simple carbohydrates are represented by monosaccharides and disaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest forms of sugar. These include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides consist of 2 monosaccharides that are linked by a glycosidic bond. These include sucrose (white sugar), lactose (found in dairy products), and maltose (found in some vegetables).
- Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) consist of 3 or more monosaccharides. These carbohydrates include starches and fiber. They are found in large quantities in legumes and cereals.
The difference between simple and complex carbs is in the speed at which they are absorbed. Complex carbs break down into simple sugars during digestion, then are absorbed into the small intestine, enter the bloodstream, and get into the liver. There, simple sugars are converted into glucose, which is carried throughout the body along with the bloodstream and serves as a source of energy.
Unlike complex carbs, simple carbs, don’t need to break down into simple sugars. They are absorbed immediately, cause a quick burst of energy, and can lead to a sharp increase in blood sugar levels. But this feeling doesn’t last long. The burst of energy will soon be replaced by the feeling of tiredness. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are absorbed gradually, and increase sugar levels gradually too — that’s why they serve as a more stable source of energy for the body.
What the benefits of complex cars are
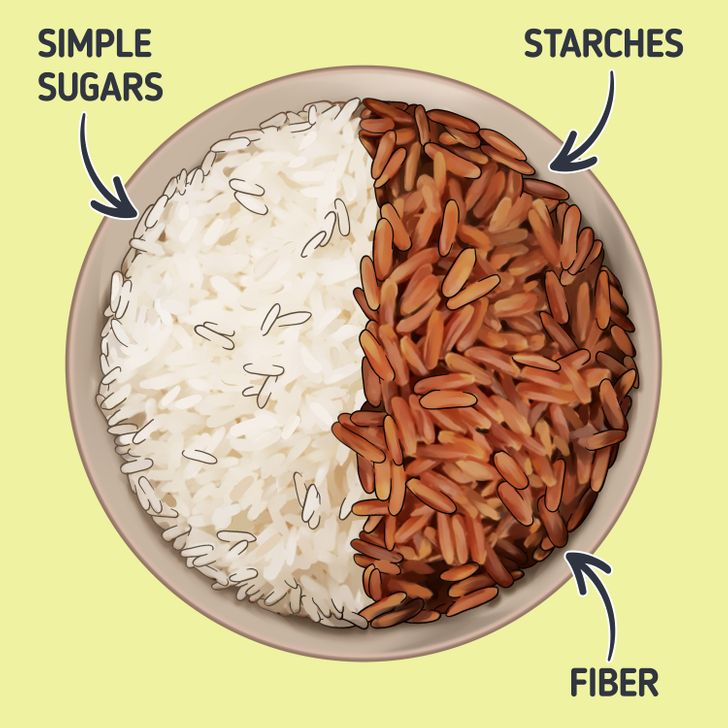
As we mentioned, complex carbs are represented by starches and fiber in food. Starches are found in foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains. In addition to carbs, they contain vitamins and minerals that your body also needs.
The same foods that contain starches serve as a source of fiber. It is difficult for the body to break it down into simple substances, so most of the fiber passes through the intestines undigested, which stimulates its work and helps the body to perform its functions.
Finally, both starches and fiber require more time for digestion. Therefore, they keep you feeling full longer, stabilize blood sugar levels, and reduce the pressure on the pancreas, which secretes the insulin hormone every time it becomes necessary to deliver glucose to the cells of the body.
How many carbs a day do we need
The recommended amount of carbs per day for adults is 135 g (4.76 oz), but this is only an approximate number. The exact amount depends on the characteristics of the diet, its calorie content, a person’s age, gender, physical activity level, weight, and health. For example, for people with diabetes, doctors may recommend limiting the daily intake of carbohydrates, and, on the contrary, increasing it for pregnant women.
In general, the ratio of carbs for most people should be 45-65% of the total daily calorie intake. 1 g (0.03 oz) of carbohydrates equals approximately 4 cal, so the 1,800 cal that we intake per day should ideally contain between 202 g (7.13 oz) and 292 g (10.3 oz) of carbs.
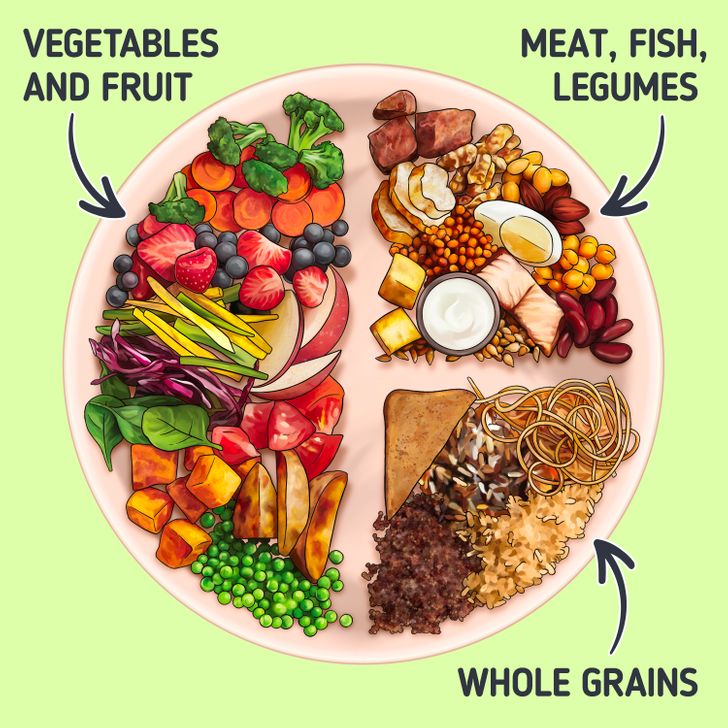
However, the count of calories and ratio of carbs in the diet can be quite a difficult task to do. In this case, you can take the “healthy plate” as a reference:
- 1/2 of your plate should be fruits and vegetables
- 1/4 — whole grains
- 1/4 — meat, fish, beans, eggs, or dairy
What sources of carbs should you choose

Sources of complex carbs:
- Beans: black beans, chickpeas, lentils, peas, peanuts.
- Fruits: apples, peaches, melons, citrus, pears, and bananas.
- Whole grain products: brown rice, oatmeal, quinoa, and other grains as well as corn, whole-wheat bread, and pasta.
- Vegetables: potatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, zucchini, and any greenery.
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds.
What sources of carbs should we avoid
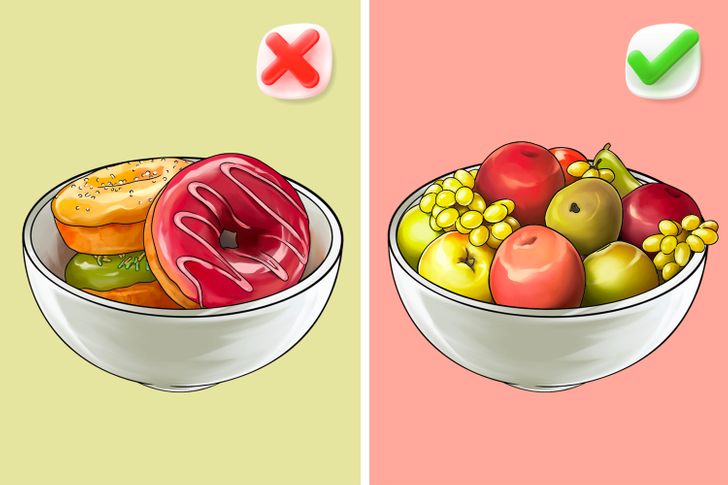
Apart from starches and fiber, vegetables and fruits contain many simple carbohydrates. But still, this food is useful due to the vitamins and minerals it contains. Therefore, when speaking about the dangers of simple carbohydrates, experts don’t mean simple carbs themselves, but added sugars. They are found in industrially processed food, which we see in large quantities on store shelves. Due to its low nutritional value, it is often referred to as “empty calories” and is considered one of the risk factors for excess weight.
Products with added sugars are:
- sweets and products from the bakery
- ice cream
- canned products
- juices, lemonades, and soda drinks
- corn flakes
- syrups
- white bread
- yogurts with additives
- potato chips and various snacks
It’s better to limit the consumption of these products. It will help you maintain your daily carbohydrate intake, keep your blood sugar stable, and avoid health risks.
Carefully read the ingredients before purchasing to control the amount of added sugars in your diet. Remember that sugar can disguise itself under different names, for example — dextrose, fructose, sucrose, molasses, agave nectar, honey, cane sugar, or corn syrup.