How Your Brain Works
The human brain is a unique organ that still holds a lot of mystery and we already know quite a bit about it. For example, scientists found out that the brain has regions, and each of them has its own function.
With 5-Minute Crafts, you will find out how your brain works and what different parts of it do.
What the brain is
The brain is the organ that controls a person. It’s responsible for our thoughts, memory, speech, movements, and the work of many organs. The brain gets information from the 5 senses: vision, smell, touch, taste, and hearing.
Our brain consists of 2 types of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and glia cells. The neurons transmit information through electric and chemical signals. And the glia cells provide nutrition, protection, and structural support for the neurons.
Anatomy of the brain
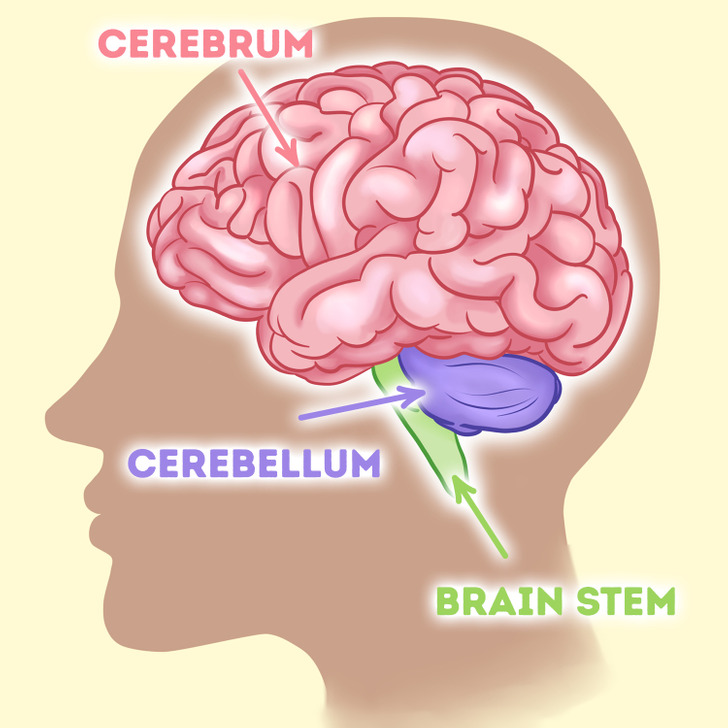
The human brain weighs around 3 pounds and consists of 3 main parts.
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and it includes 2 hemispheres and some other structures. It helps us see, feel, hear, make judgments, learn, show emotions, and control our movements.
- The cerebellum is under the cerebrum. It coordinates muscle movements and is responsible for posture and balance.
- The brain stem connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It’s responsible for breathing, heart rate, digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting and swallowing, body temperature, and sleep cycles.
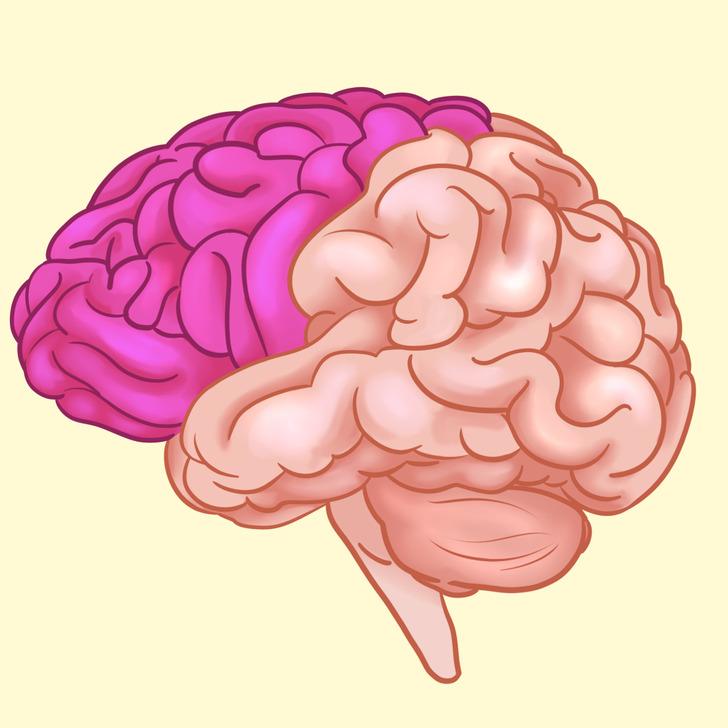
2 hemispheres
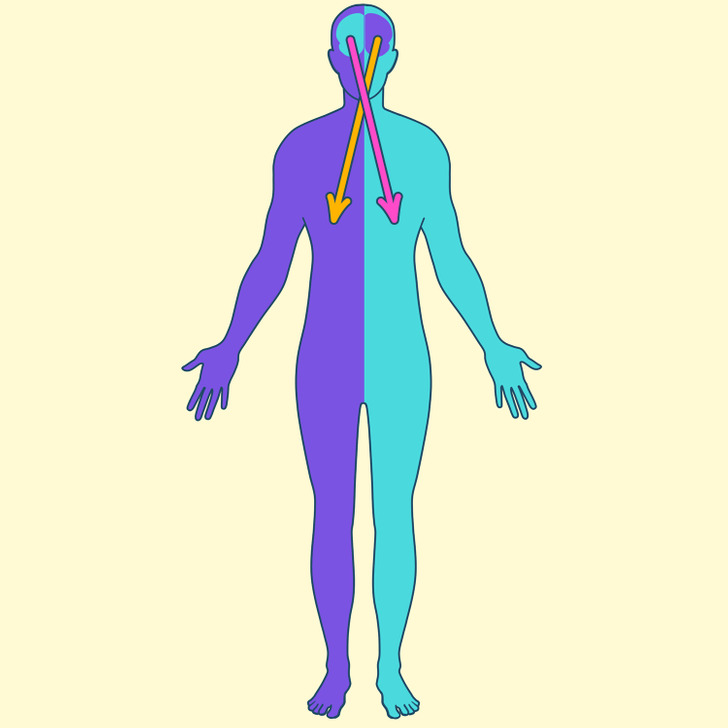
The cerebrum has 2 hemispheres: the right one and the left one. They are joined by a bundle of fibers called the corpus callosum that transmits messages from one side to the other. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body.
- The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body. Usually, it’s dominant and is responsible for logic and analytical thinking. It has 2 main language centers:
- Broca’s area that deals with verbal expression and speech production.
- Wernicke’s area that deals with verbal comprehension.
- The right hemisphere is responsible for the left side of the body. The right hemisphere is involved in creativity, perception, and visual-spatial processing. It is also involved in facial recognition.
What grey matter is
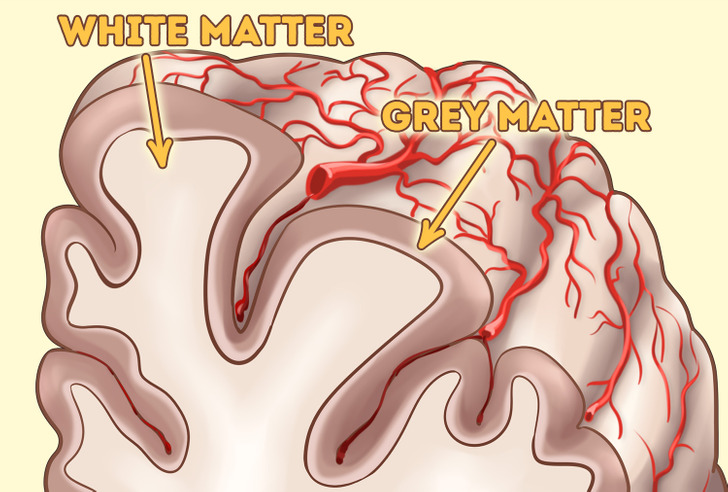
The cerebral cortex (grey matter) is the outer layer of neural tissue on the brain surface. It’s what makes every human unique. It’s where consciousness, thinking, judgment, and imagination happen.
The cerebral cortex contains 16 billion neurons and they make it grey. Under the cortex, there are long neural fibers (axons) that connect regions of the brain. They are called white matter.
You might have guessed why the brain is so curvy. Thanks to the folds, more neurons can fit into the skull which makes us more functional.
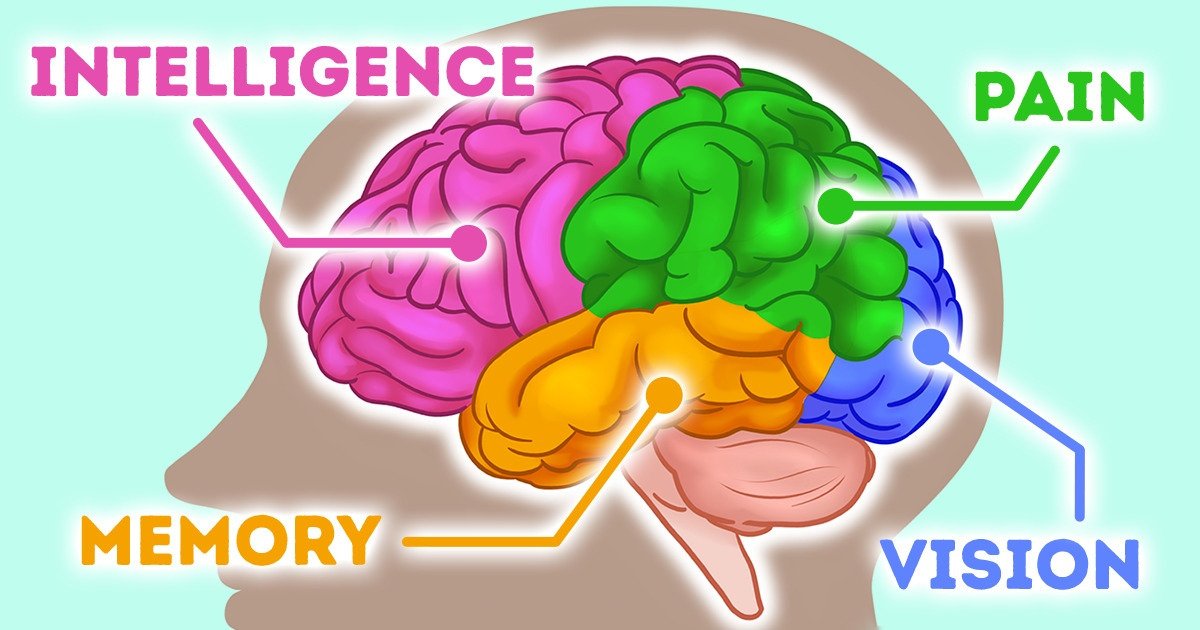
The cerebral cortex has 4 lobes:
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
- occipital lobe
- temporal lobe
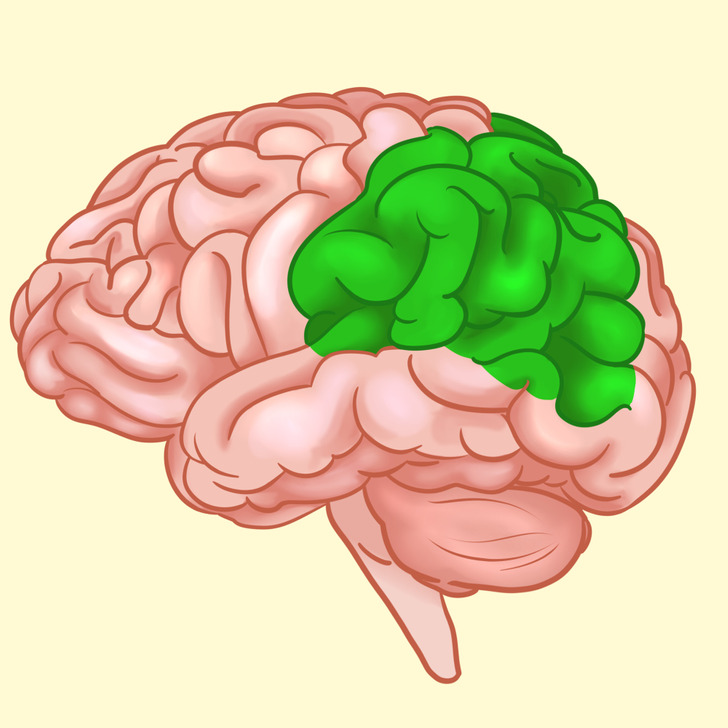
Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is in the front part of the brain and is the biggest one of all 4. It’s responsible for:
- body movement
- speaking and writing
- intelligence, concentration, and self-awareness
- temper, behavior, and emotions
- judgement, planning, and problem-solving
Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is in the middle. It’s responsible for:
- language comprehension
- interpretation of signals from vision, hearing, motor, sensory, and memory
- sense of touch, pain, temperature (sensory strip)
- spatial and visual perception
Occipital lobe
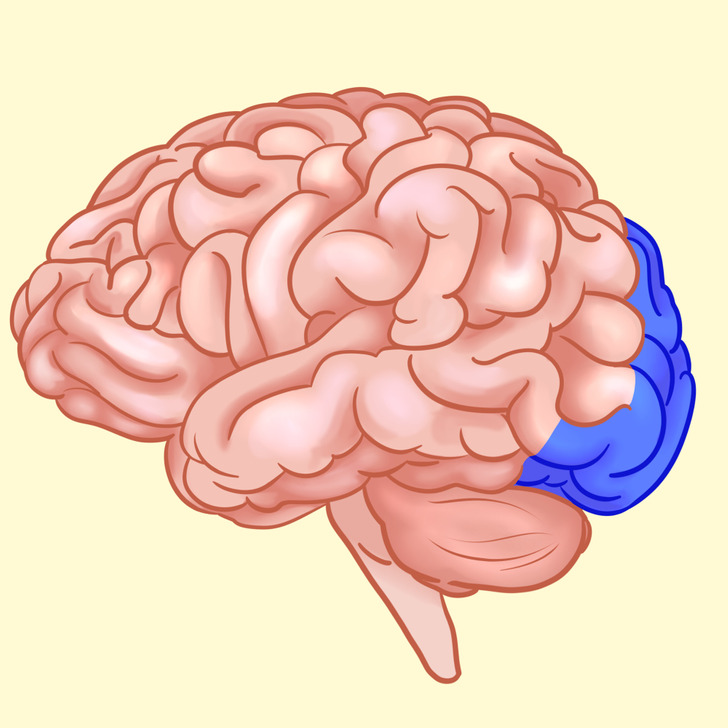
The occipital lobe is in the back of the brain. It contains the primary visual cortex, which receives and interprets information from the retinas of the eyes.
The main function of the occipital lobe is the interpretation of visual images. If it’s damaged, a person can go blind even if the eyes and the nerves are completely healthy.
Temporal lobe
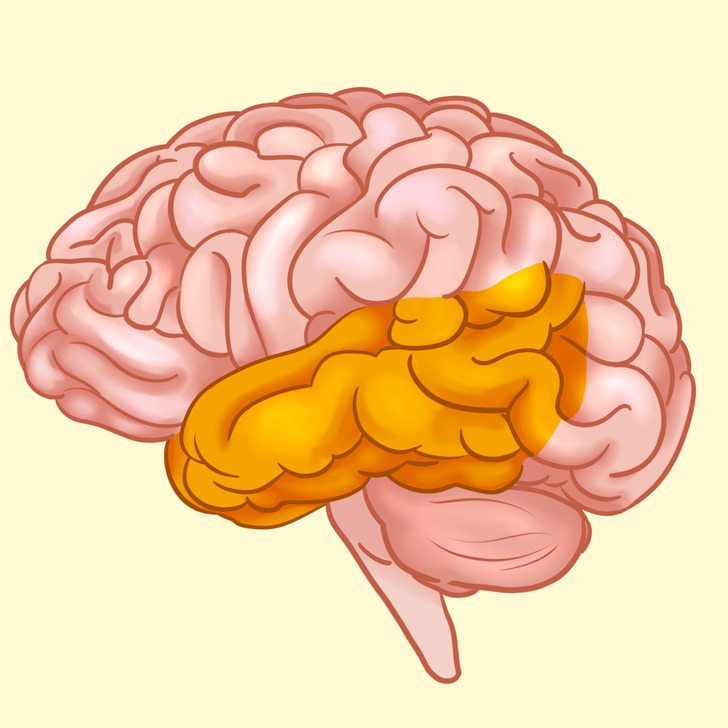
The temporal lobe is right under the temples, on the underside of the cerebrum. It helps us interpret the sounds and the language we hear. It also contains the hippocampus which is responsible for memory.
The left temporal lobe is connected with verbal memory and the right one — with music. The left one recognizes words, and the right one recognizes faces.
The temporal lobe is responsible for:
- language comprehension
- memory and its volume
- hearing
- self-organization
How the brain lobes interact
The lobes are not separated from each other and they are constantly working together to interpret and learn information.
The brain is divided into the left and the right hemispheres and each lobe crosses both of them. The brain lobes have a lot of functions and sometimes they share them. The right functioning of one area often depends on the other one. Some scientists believe that if one lobe is damaged, the others can compensate for it.