What Types of Body Fat There Are
There are different kinds of fat cells in your body, and they’re all stored in different ways. For most people, fat doesn’t have the best reputation. But for scientists, fat is actually one of the most intriguing subjects. Let 5-Minute Crafts explain what fat cells exist and how they’re stored in your body.
1. What types of body fat cells there are
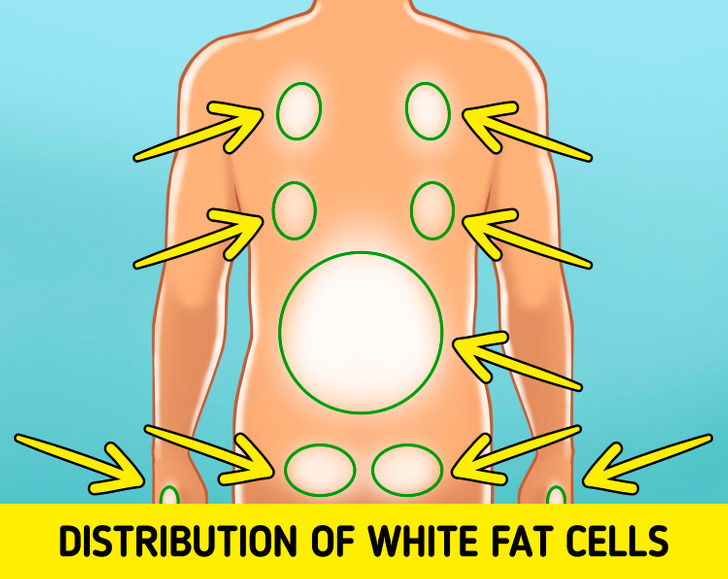
- White fat cells: These cells are your body’s way of storing energy for later. Even though some white fat is necessary to keep your body healthy, too much of it can put you at risk for some other health issues.
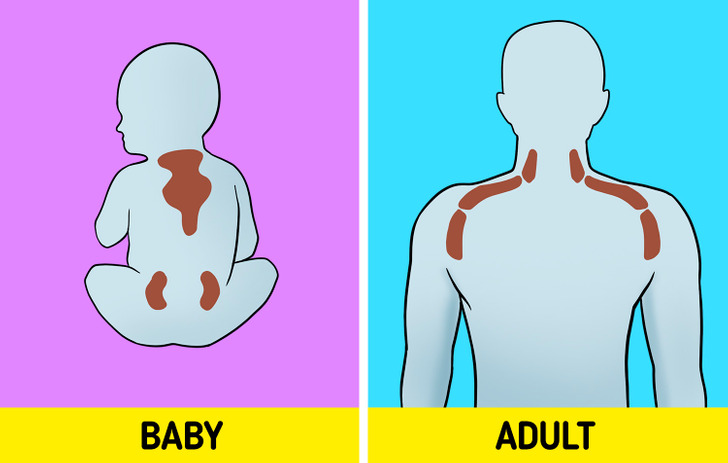
- Brown fat cells: Also known as brown adipose tissue (BAT), brown fat is “good” fat and has the ability to generate heat and burn calories. Previously, it was thought that this fat was mostly found in babies, but researchers now know that adults have some small amounts of brown fat stored in the neck and shoulders.
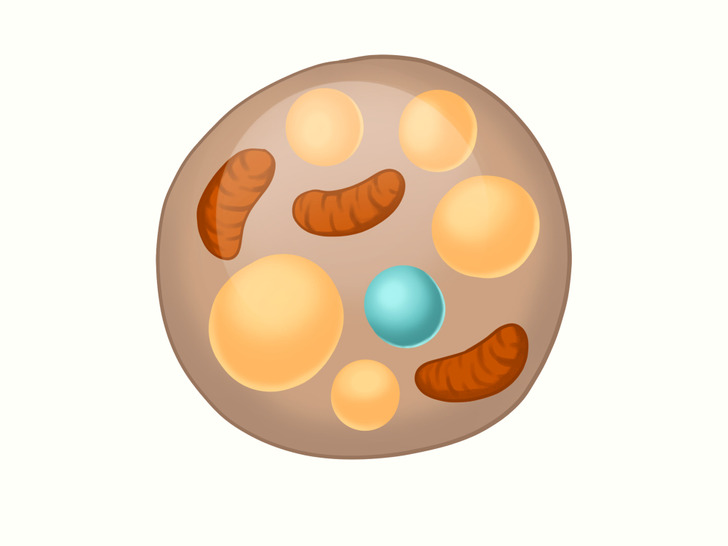

- Beige fat cells: It’s known that beige (or brite) fat cells function somewhere in between brown and white fat cells. It’s also known that beige fat cells can help burn fat instead of storing it, but it’s still under research.
2. How fat cells are stored
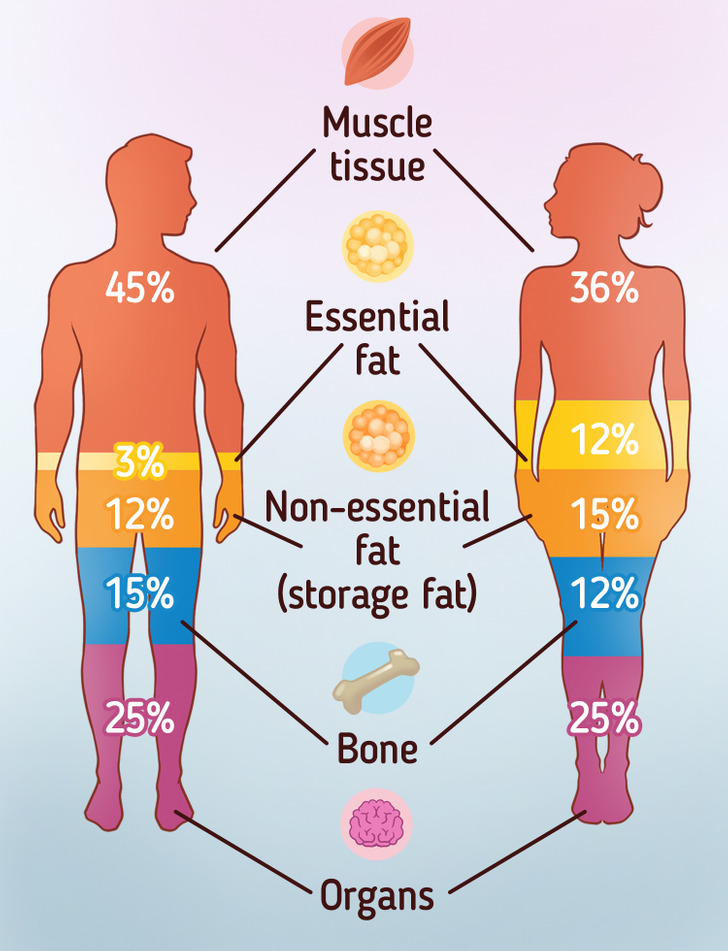
- Essential fat: This fat plays a key role in your body and overall health. It’s found in the brain, nerves, bone marrow, and membranes. It’s also important to the function of hormones (including fertility hormones), vitamin absorption, and even temperature regulation.
It’s recommended to have certain percentages of essential fat in your body to be in good health — women require at least 10% to 13%, while men need 2% to 5%.
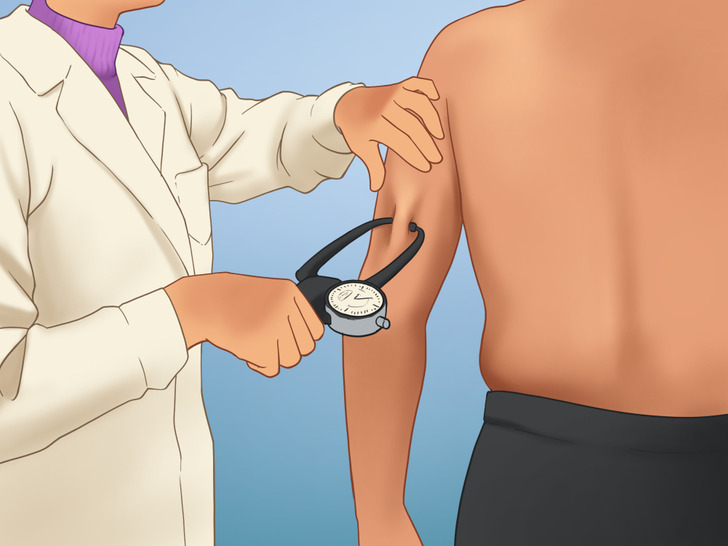
- Subcutaneous fat: Most of our body fat is subcutaneous, meaning it’s under the skin. It’s a mix of white, brown, and beige fat cells. In fact, you can pinch or squeeze it and even measure it using calipers to estimate the total body fat percentage you have.
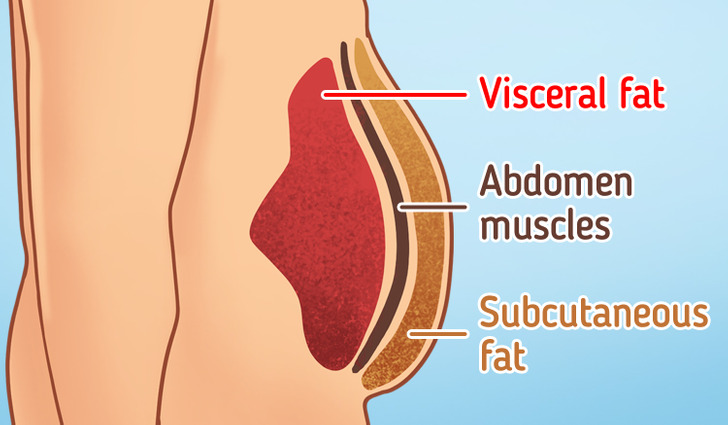
- Visceral fat: Most commonly referred to as “belly fat,” this type of fat is mainly stored in the belly and around the body’s major organs (heart, kidneys, pancreas, and intestines). However, too much of this fat can lead to health complications.
Share This Article