What Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Are, and Which of Them Is Bad for Health
Many people are interested in the healthy ratio of fat to muscle in the body. However, not everyone understands what fat is and why it’s needed. Meanwhile, there are several types of fat in our bodies.
5-Minute Crafts would like to tell you about types of body fat and what their functions are.
What fat is
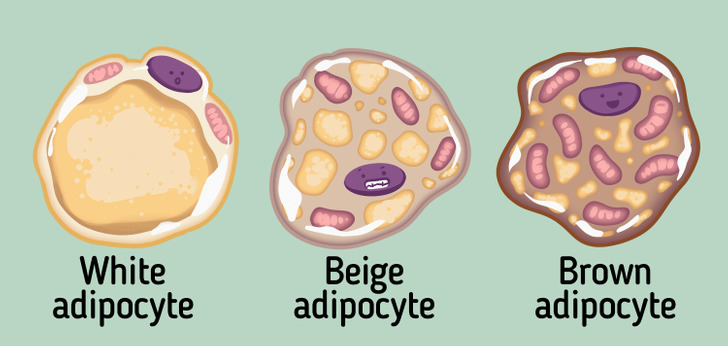
Body fat is a connective tissue made up mainly of adipocytes. Adipocytes are cells that store energy. They contain lipid droplets, which are large globules of fat surrounded by a structural network of fibers.
Depending on their origin, location, and function, adipocytes are divided into 3 different cell types:
- White
- Beige
- Brown
There are 2 types of adipose tissue: white and brown. The white one consists of white and beige adipocytes, and the brown type consists of brown ones.
White adipose tissue is most abundant in our bodies.
Where fat is located
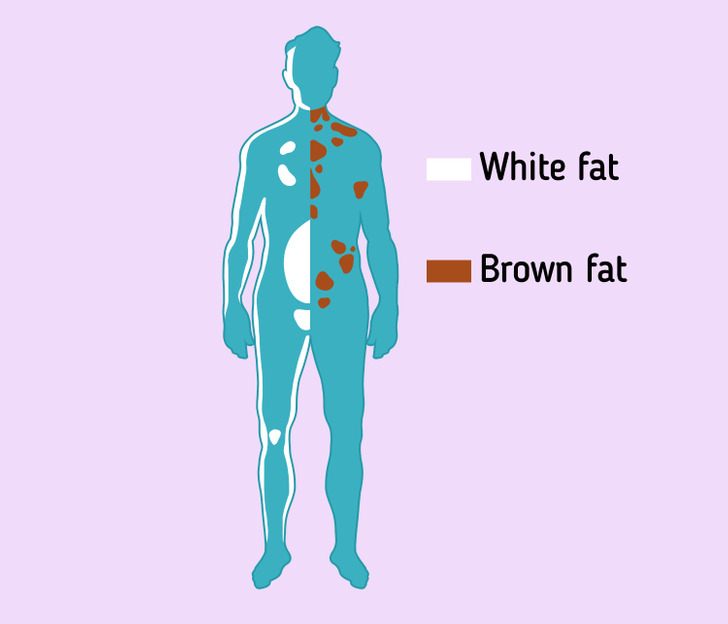
Fat can be found in different parts of the body. White adipose tissue is found in subcutaneous, visceral, and bone marrow fat.
There is not as much brown fat in adults as in children. Newborn babies have it mainly on the back, along the upper half of the spine, between the shoulder blades, and around the kidneys. Adults have brown fat around the internal organs, in the region of the anterior muscles of the neck, the supraclavicular fossa, as well as under the collarbone, armpits, at the anterior abdominal wall, and in the inguinal fossa.
In a healthy adult, adipose tissue usually comprises 20%-25% of the total body weight. However, this ratio can vary from less than 10% to more than 40%.
Functions of fat
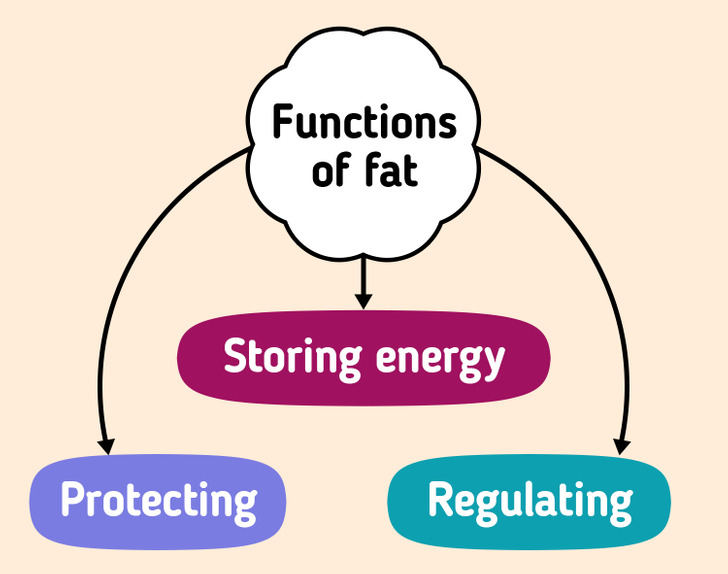
- Storing energy: The calories received and unused are sent to adipose tissue. And the body uses this energy at the right time, like when we sleep, work, or run. Fat is the main form of energy storage in our body.
- Protection: Fat protects our organs and also helps maintain the right body temperature. A layer of subcutaneous fat protects us from uncomfortable temperatures, helping to maintain our microclimate.
- Producing and regulating hormones: Adipose tissue secretes leptin, a hormone that helps regulate appetite. Fat plays a big role in reproductive health. For example, if a woman doesn’t have enough body fat, she may have problems with conception.
Types of fat
There are 2 types of fat in the human body:
- Subcutaneous
- Visceral
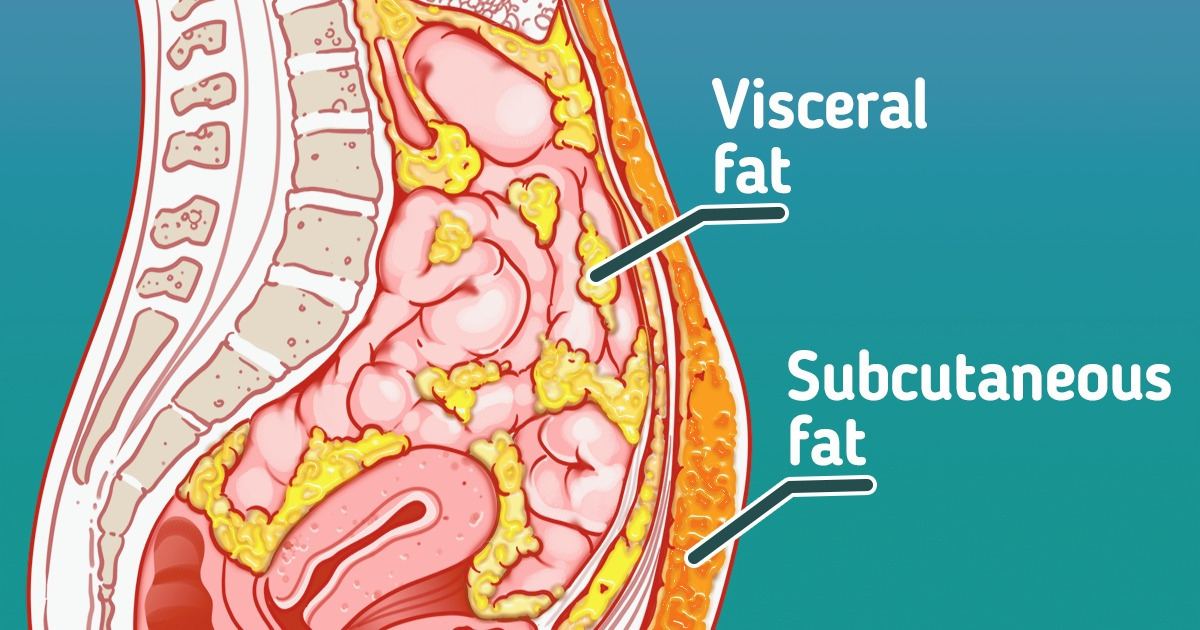
Subcutaneous fat
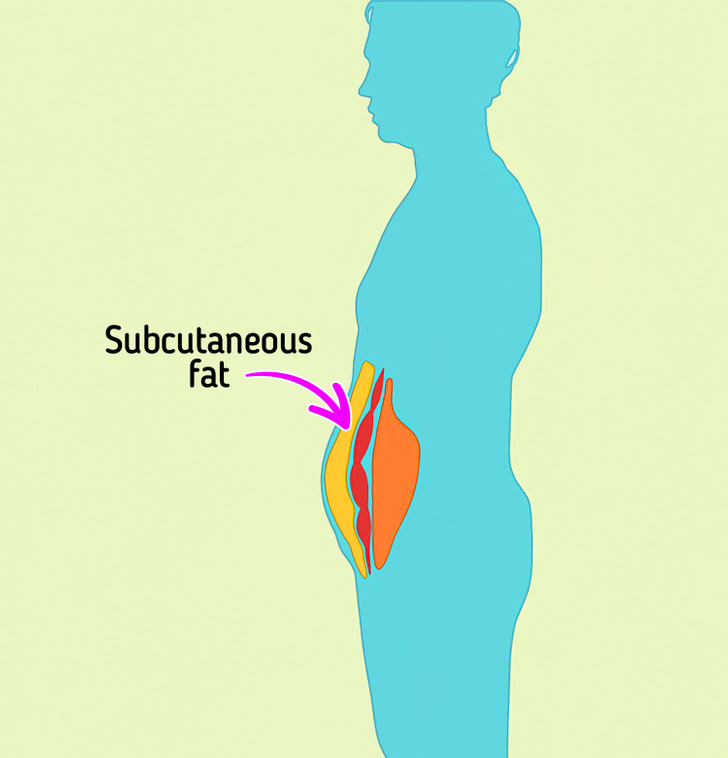
Subcutaneous fat is found almost all over the body between the skin and the underlying muscles. It is the layer of subcutaneous fat that connects the epidermis to the muscles.
In men and women, the distribution of subcutaneous fat is different. Women usually have more of it on the hips.
Methods for measuring subcutaneous fat levels:
- DeXA is a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry performed by a clinician.
- Hydrostatic weighing is carried out underwater in a laboratory.
- Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) is available on some models of home scales. Such devices show weight, body fat percentage, and other body parameters. However, this method is not the most accurate.
- Calipers can be used to measure the level of fat, as they can pinch the fat tissue in certain areas of the body. This should be done by a skilled practitioner for the most accurate results.
Visceral fat
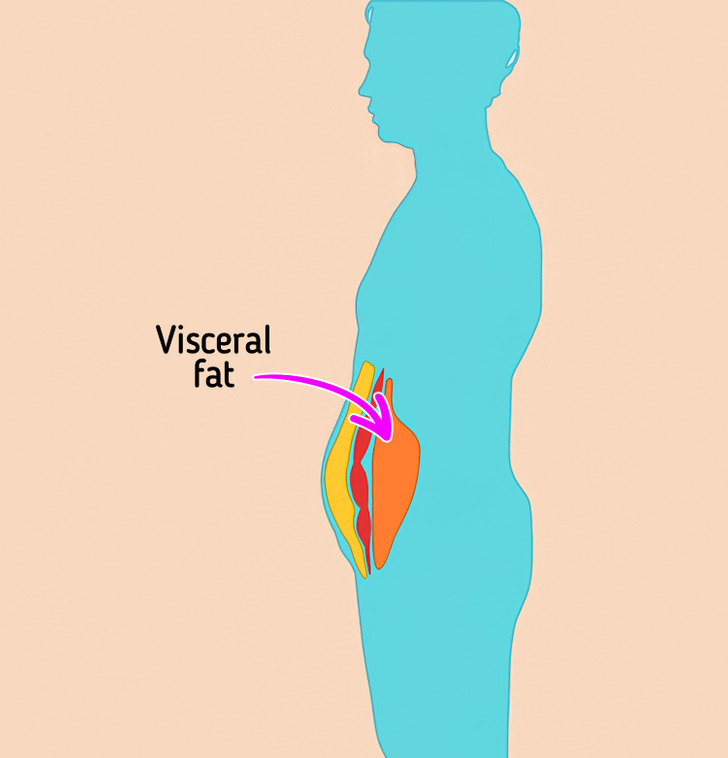
Visceral fat is the fat that coats the internal organs. Even slender people with a flat stomach have it. Its level in the body can only be determined with a special bioimpedance scale. This is a device that measures body weight by sending a weak, painless current through the body.
The most obvious outward sign of excess visceral fat is a potbelly. People with the “apple” body type often have excess fat in the abdominal cavity.
Visceral fat levels tend to rise with age.
What the dangers of excess fat are
We have already mentioned above that every person has fat, and this is absolutely normal. However, an excess of adipose tissue is often associated with various diseases. Physicians believe that excess visceral fat can be the cause of diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and dementia.
How to maintain a normal level of fat in the body

To maintain normal body fat levels, it’s recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat a healthy diet, and exercise.
If you think you have too much adipose tissue, consult a doctor, who, if necessary, will make a special diet for you and select a set of exercises. Perhaps you’ll have to change certain habits since poor sleep and stress contribute to fat storage.