Why Blood Is Red, and Veins Are Blue
Some children’s questions can even confuse adults, because the answers to them are not that obvious, and can make you have to think really hard (and maybe even do some research).
5-Minute Crafts wants to answer the question about why blood is red and veins are blue.
How blood circulates in our body
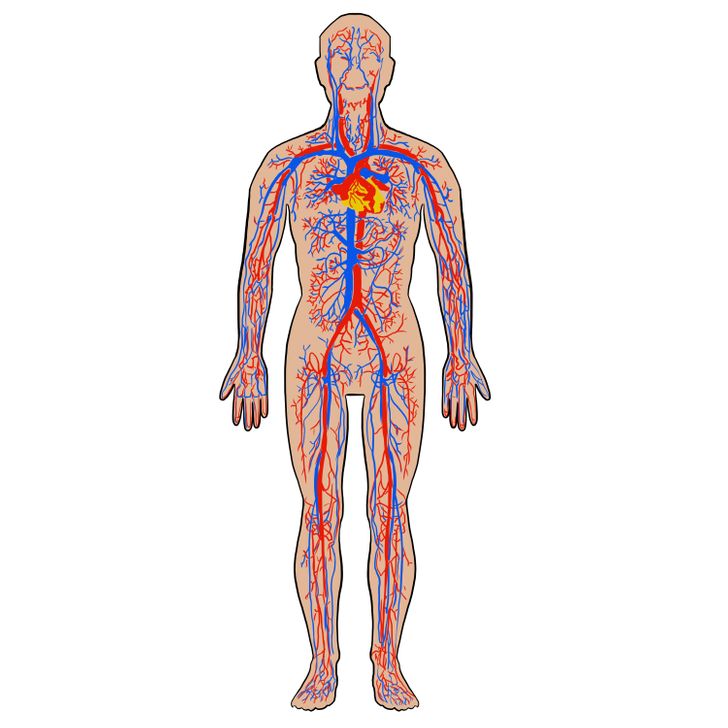
Blood vessels run through the entire human body, providing continuous nutrition to the organs and tissues. The heart is the central organ of the circulatory system that acts like a huge pump, pumping blood through the body.
Oxygenated blood is carried from the heart through the large vessels, called arteries, which, in turn, redirect it to smaller vessels — called capillaries. Capillaries deliver oxygenated blood to the most distant parts of the body, feeding the cells, and then they carry the “waste” blood that is saturated with carbon dioxide into the veins. Through the veins, the blood returns back to the heart, in order to then pass through the lungs again, get oxygenated, and begin the next cycle.
Is venous blood blue?
Some people think that venous blood is blue due to the lack of oxygen in it, which is why veins look bluish. However, this assumption is wrong. In fact, blood is always red. Arterial oxygen-rich blood has a bright red color, while venous blood, which has almost no oxygen, is dark red.
So, why do veins look blue?
Why veins look blue
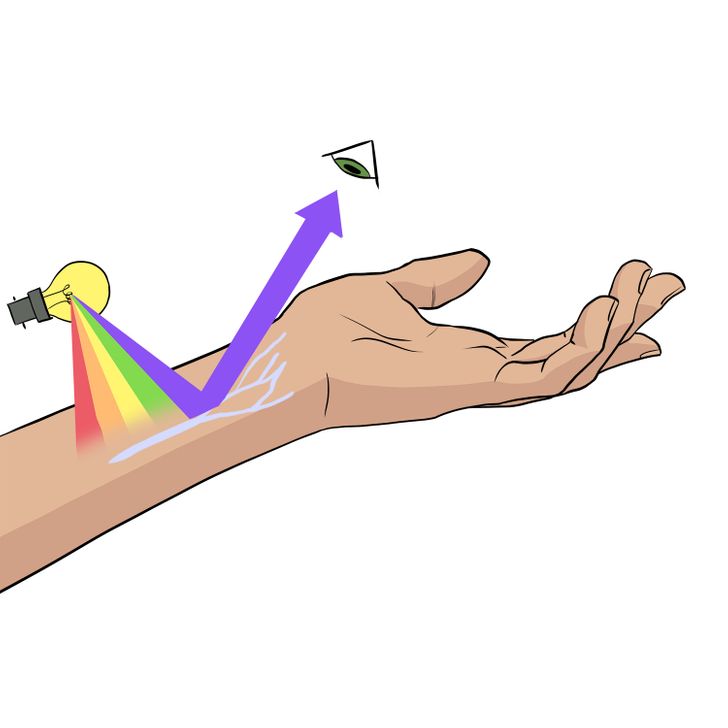
The color of veins depends on several factors: the way light behaves when it comes into contact with our body, the ability of our eyes to perceive colors, and the special properties of blood.
Different colors of light have different wavelengths, which affect its ability to penetrate our skin. The light that hits our skin during the day is white. It’s a mixture of all the other colors of visible radiation. To understand why veins look blue, it’s important to figure out how the red and blue spectra of light behave.
Blue light has a short wavelength. It’s unable to penetrate deeply into the skin, therefore, when it hits it, it’s mostly reflected back. Red light has a long wavelength. It passes through obstacles more easily and is less reflected from them. This light easily penetrates 5 to 10 millimeters below the skin, where there are many veins. There, the red light is absorbed by the blood.
When red and blue lights hit the skin simultaneously (as they do every time you are in the daylight), the large veins will reflect blue light and absorb red light. At the same time, the human eye will be able to see less red color and more blue color at the location of the veins.
It’s interesting that the color of the vessels will directly depend on their size and the depth of their location. Very thin capillaries close to the skin’s surface won’t have the same deep blue hue as larger veins. For our eyes, their color might have a pinkish or purple hue.