Why Heating Food Can Cause Nutrient Loss and What You Can Do to Avoid It

Cooking food improves digestion and increases the absorption of many nutrients, but surprisingly, the way it is cooked has an important effect on the properties of the food. Therefore, it is important to know the benefits and disadvantages of each method.
5-Minute Crafts wants to show you how the method of preparation affects the nutritional content, and some useful tips for preserving nutrients.
Why food loses some of its nutrients when heated
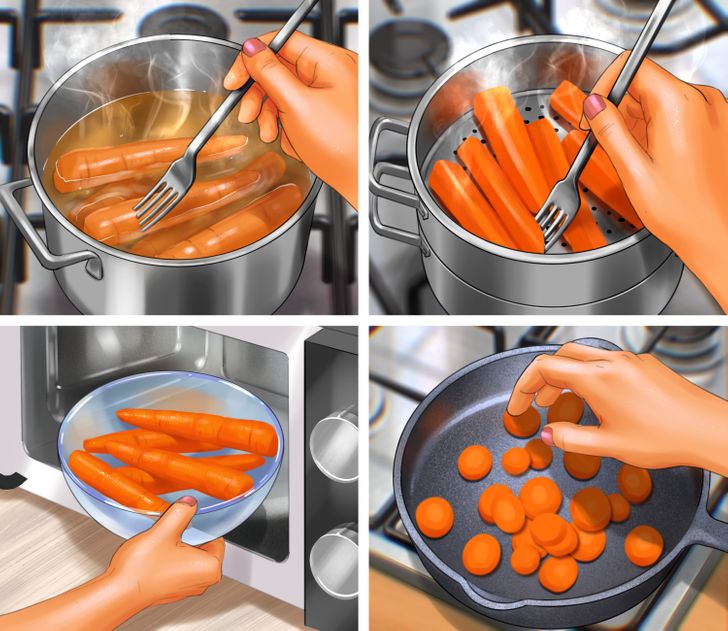

Any of the methods used when cooking can have an impact on the properties of the food you’re either boiling, frying, steaming, or even microwaving. In fact, not only are there variations in vitamins and nutrients, but also in texture, flavor, and color as you probably already know. Eating a cooked carrot is not the same as eating a raw one.
Some cooking methods can affect several key nutrients needed by our body to develop and function properly. These effects depend on the time taken to cook the food, the temperature to which the products are exposed, the cooking method, the amount of food being cooked, and of course, the food itself.
Heating food in the microwave
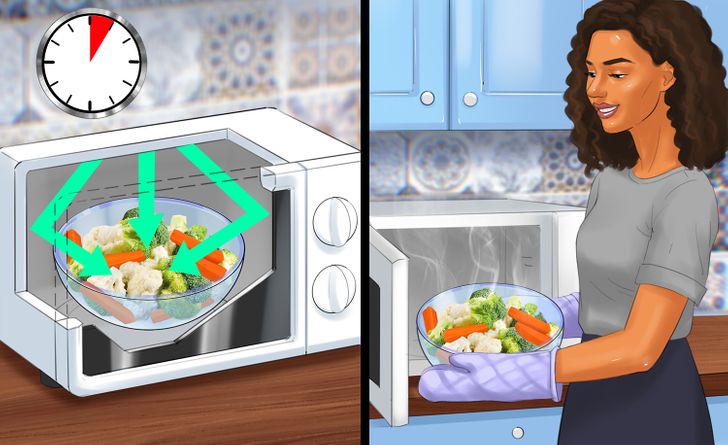
You might find this surprising, but microwaving is one of the least nutrient-damaging forms of cooking. This is because the longer it takes to cook food, the more nutrients you tend to break down and vice versa. If you take that into account, it’s clear that microwave cooking is not only fast, but also has nutritional advantages such as:
- Preserving vitamin C because cooking times are shorter, and this nutrient breaks down when exposed to heat for long periods of time.
- Retaining antioxidants in vegetables or at least doing so more than with other ways of cooking vegetables or other foods. This could be boiling or even pressure cooking.
- Having minimal effects on proteins, lipids, and minerals. And there are no significant nutritional differences between foods prepared by conventional and microwave methods.
Cooking or boiling food
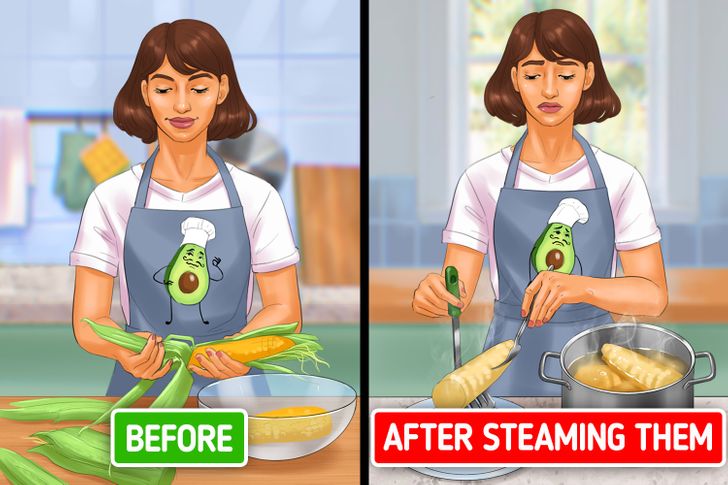

By boiling or steaming food, you don’t need to use any additional fats, which is a great advantage. However, it causes a high loss of water-soluble vitamins that remain in the liquid when the food is boiled. Because of that, this cooking methods comes with some disadvantages, like:
- Reducing the vitamin C content of the foods you boil or steam more than other methods, as this nutrient is both heat-sensitive and water-soluble. In vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and lettuce you lose about 50% of the original content of the vitamin C.
- Decreasing vitamin B levels when boiling vegetables and rice due to high temperatures, the pH, and the amount of chlorine in the water you use.
- Affecting the nutritional composition of soluble compounds like carbohydrates (sugars and soluble fiber) in edible plants, like corn.
- Changing physical properties like color, hydration, and cellular integrity of some vegetables.
Frying food
This way of cooking food is fast and convenient and comes with the added benefit of giving extra flavor to most meals. However, it’s a well-known fact that fried and deep-fried food is high in calories and trans fats that can have a negative impact on health. Here are some of the positive and negative effects of frying:
- It preserves vitamin C and vitamin B (thiamin) concentrations due to the high temperature and short time in the frying process.
- Has little or no impact on protein and minerals in fried foods.
- Provides higher energy density due to the high calorie content.
- Increases fiber in potatoes by converting starch to resistant starch.
- Toxic substances called aldehydes can be formed. This happens when the oil is heated at a high temperature for a long period of time.
Steaming
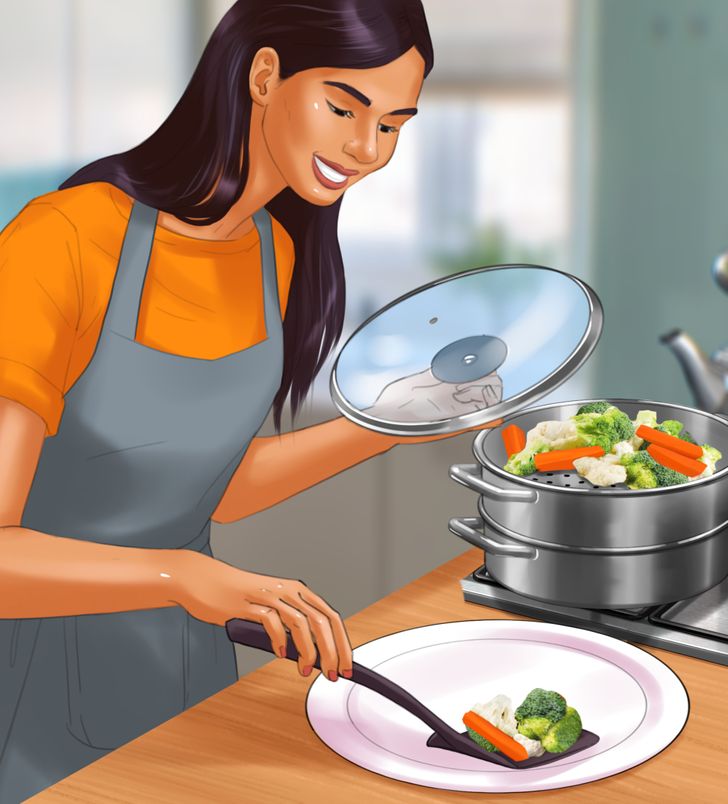

Steaming is one of the best methods to preserve food nutrients, especially for vegetables. Some of the benefits and disadvantages of this method are:
- It maintains a high amount of vitamin C. In vegetables like broccoli, spinach, or lettuce, only 14.3, 11.1, and 8.6 % are lost, respectively.
- It produces a change in the sensory properties of appearance, texture, and flavor. Although in most vegetables, these changes are widely accepted by most people.
- Retains certain nutrients in cooking broccoli like chlorophyll, soluble proteins, and soluble sugars.
Tips to prevent nutrient loss during cooking

There are many ways to preserve the nutritional content of food without losing the flavor or other qualities. And while any cooking method has an impact on the properties of the food, there are some recommendations to maximize nutrient retention:
- Avoid peeling vegetables until after cooking or, better yet, do not remove the peel at all, to increase the fiber and nutrient intake.
- Cut foods after cooking them, since when cooked whole, they don’t have as much exposure to heat.
- Cook animal protein sources in the shortest possible time and at a high enough temperatures (about 75°C) to kill harmful organisms and preserve nutrients. This is the best way to make sure eating protein is safe, while at the same time you still get enough nutrients to make the meal worth it.
- Eat cooked vegetables within one or 2 days, as the vitamin C content decreases with exposure to air. Ideally, you’d eat them right after they’ve been prepared.