How to Grow Trees From Cuttings to Turn Your Garden into a Magical Haven
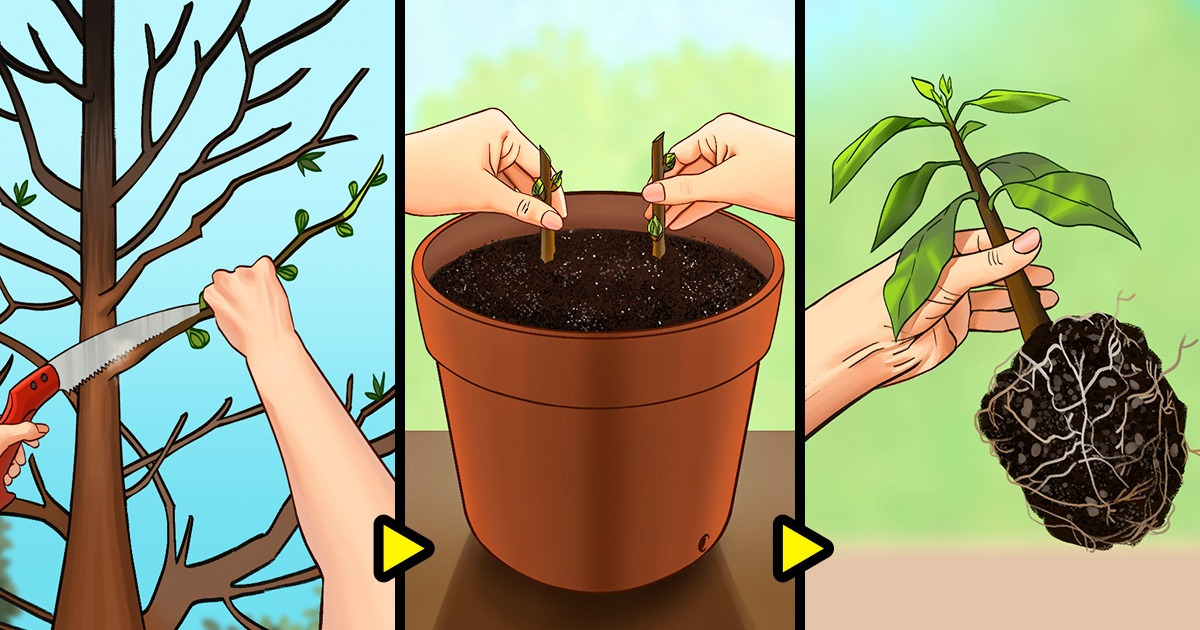
Hardwood cuttings are pieces of firm stem that can be taken when a plant is dormant. They’re one of the simplest propagation methods as maintaining them doesn’t require high humidity levels. Moreover, this technique will not only allow you to grow trees, but also other types of plants, including shrubs and climbers.
5-Minute Crafts will teach you the correct way to take hardwood cuttings and how to propagate them.
When and how to take cuttings:
You can take hardwood cuttings during the dormant season, ideally, from mid-autumn until late winter, either right after the leaves fall or just before the buds start bursting. Even though it can take hardwood cuttings a long time to grow shoots and roots, this is generally a successful technique.
❗Remember to avoid taking cuttings during periods of severe frost with temperatures below 23ºF (-5ºC).
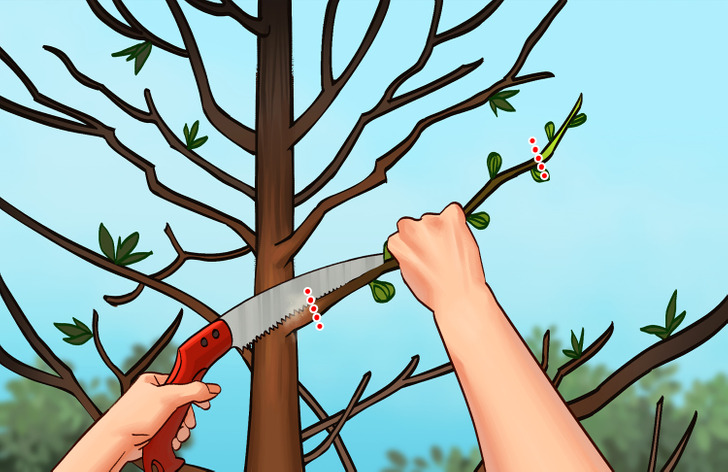

Step 1: Choose suitable cuttings that are near pencil-thickness from their growth in the current season. They will look mature and woody rather than green and soft. Remove any unripened green wood at the top.
💡Increase the chance of rooting tree branches by taking cuttings where the current season’s branches meet 2-year-old wood.

Step 2: Trim the cuttings to an appropriate size by making a horizontal cut at the base, about 6 mm (0.25 inches) below where the lowest bud is. Look for a bud around 15-20 cm (6-10 inches) away from the base end to cut the tip. Make a diagonal cut 6 mm (0.25 inches) above the tip bud.
💡Hardwood cuttings are usually cut much longer than other types of cuttings as these need more time to develop roots, which means that they have to use the food supplies located in the cutting to keep these roots alive during winter. Longer cuttings can store more food than shorter ones.
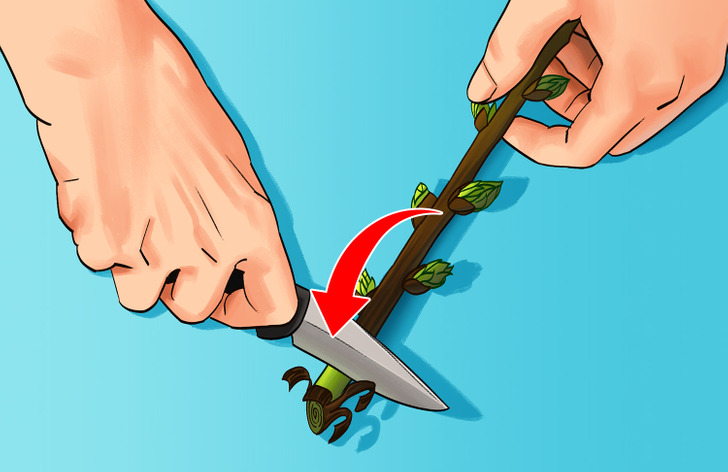

Step 3: Remove a thin layer of bark at the base of the cutting to expose the cambium, which is the light green layer found right under the bark when scraped away.
💡 This will encourage rooting and eliminate any physical barrier that could prevent roots from forming.
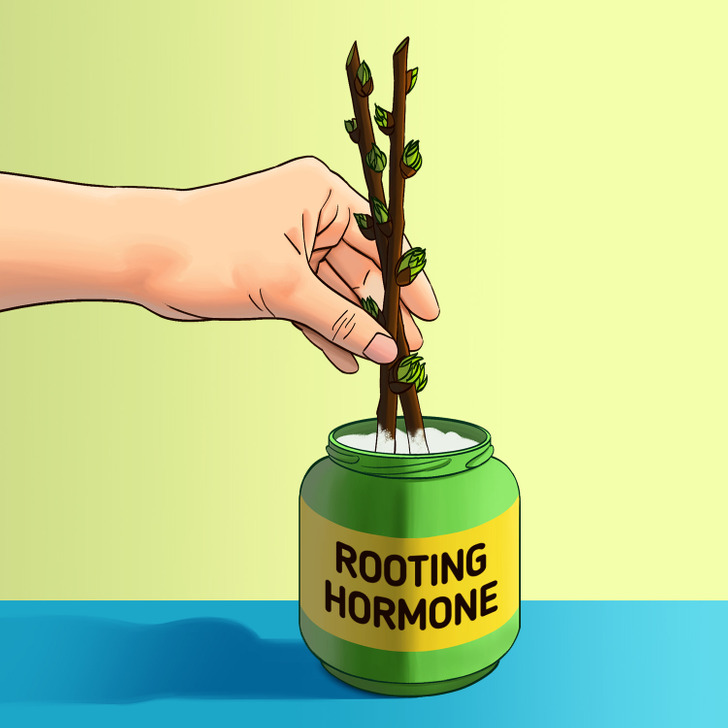
Step 4 (optional): If you want to encourage root growth, you can use rooting hormone by placing the bottom of the cuttings into the product. If you opt for using root hormone powder, make sure to remove the excess product by tapping the cuttings.
How to plant the cuttings:
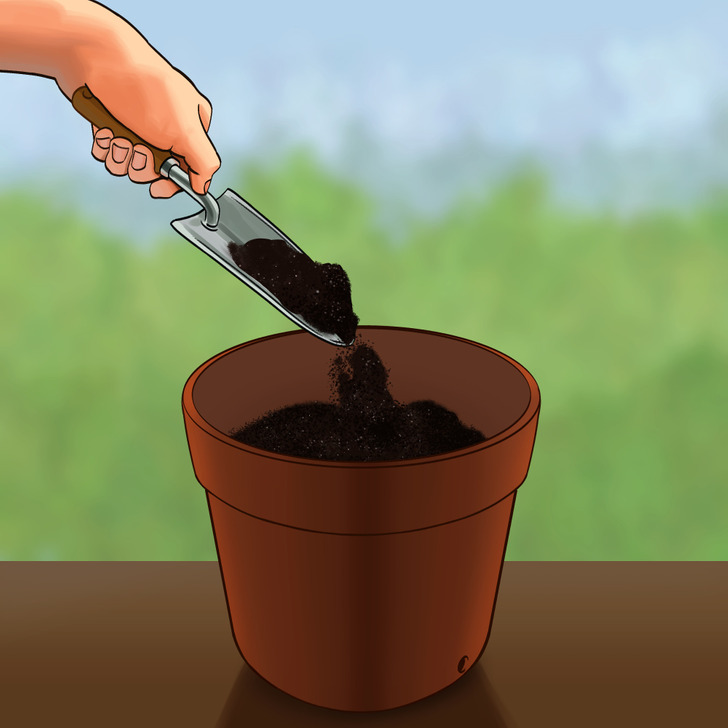

Step 1: Fill a pot with propagating medium. Some materials usually used for this purpose are coarse sand, coconut coir, regular potting mix, or mixtures that are equal parts of peat and Perlite, or equal parts of peat and sand (both by volume).
✅ You may also use equal parts of multi-purpose compost and coarse grit.
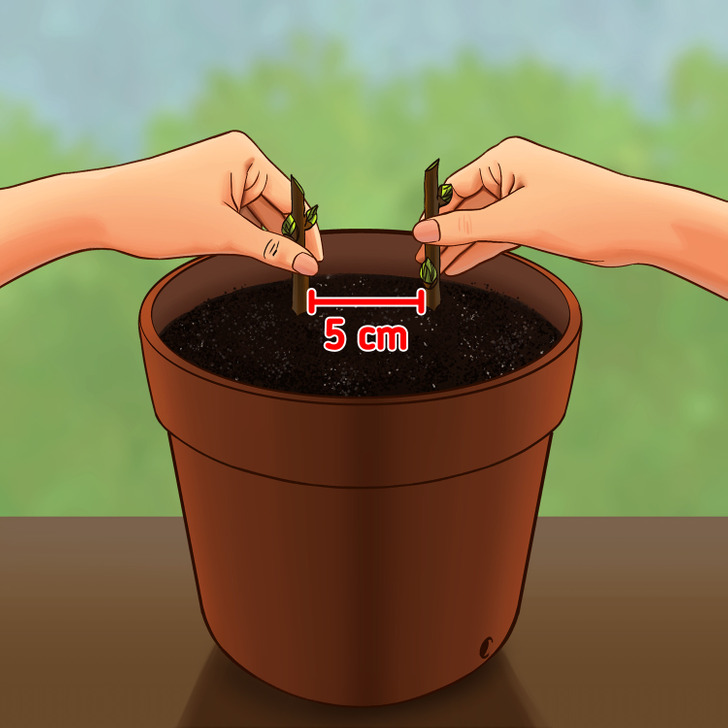

Step 2: Put the cuttings into the pot so that 2/3 of each is below the propagating medium. Make sure to place them separately by leaving 5 cm (2 inches) between them. Then, press the soil down around the cuttings.
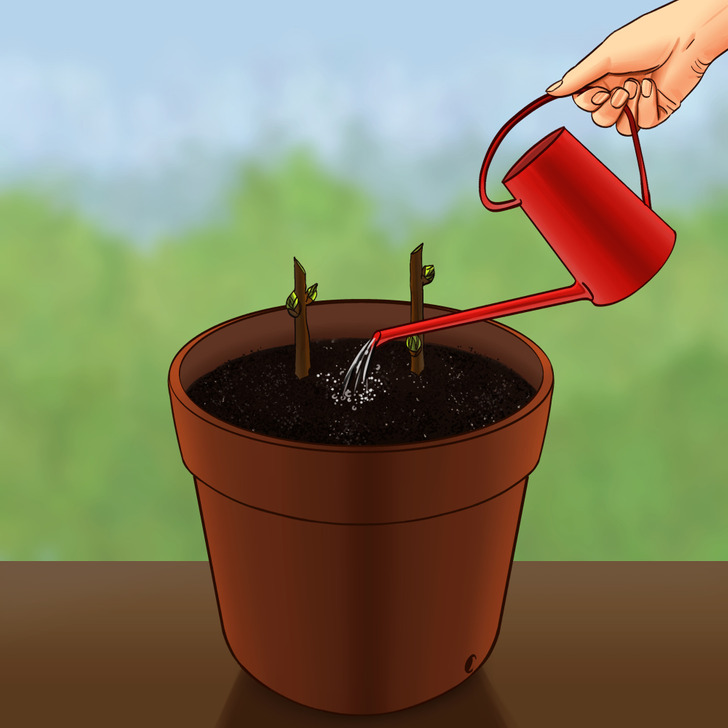

Step 3: Water the propagating medium around the cuttings regularly to keep it slightly damp. However, make sure to not overwater, as this may lead the cuttings to rot. If possible, put the pot in a cold frame to encourage root growth. Your cuttings will be in good condition for transplanting in the spring.
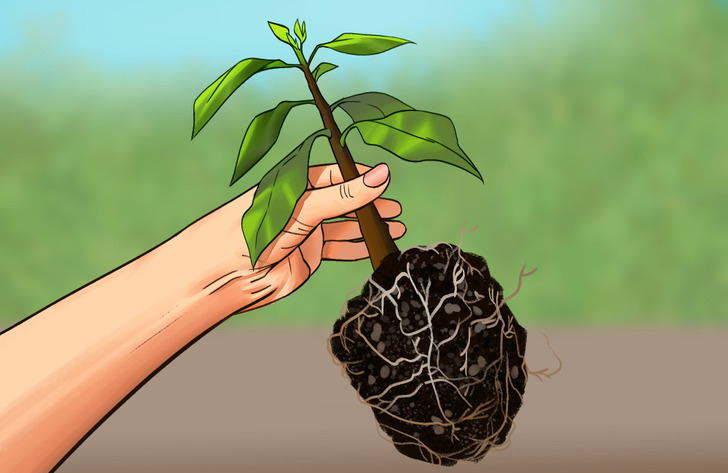

Step 4: Surviving cuttings that finally root should have new leaves during the spring. Do not try pulling them out, as the new roots will be fragile and can be easily damaged. Wait until healthy roots are coming out from the pot’s drain holes and carefully remove the cuttings to transplant them into their pots or in your garden.
Bonus: Which plants are suitable for this technique.
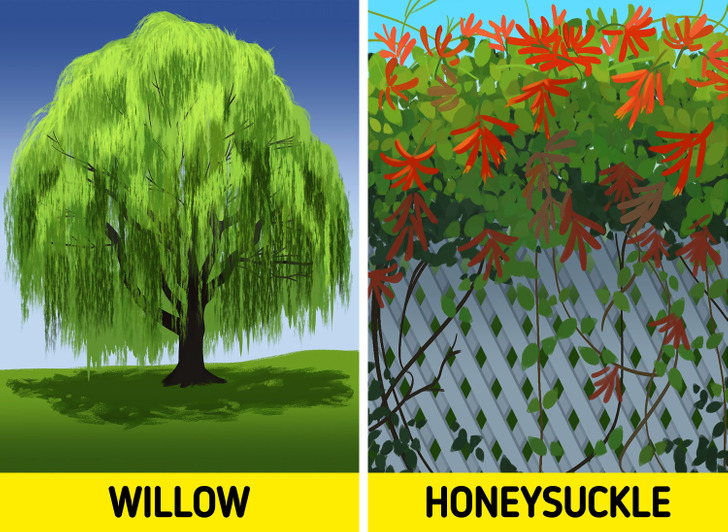

- Trees, like planes, poplars, and willows.
- Deciduous shrubs, like dogwood, rose, mock orange, flowering currant, and butterfly bush.
- Climbers, like honeysuckle and vines.
- Fruit, like red, black, and white currants, figs, mulberries, and gooseberries.