A Guide to How Long Different Dog Breeds Live
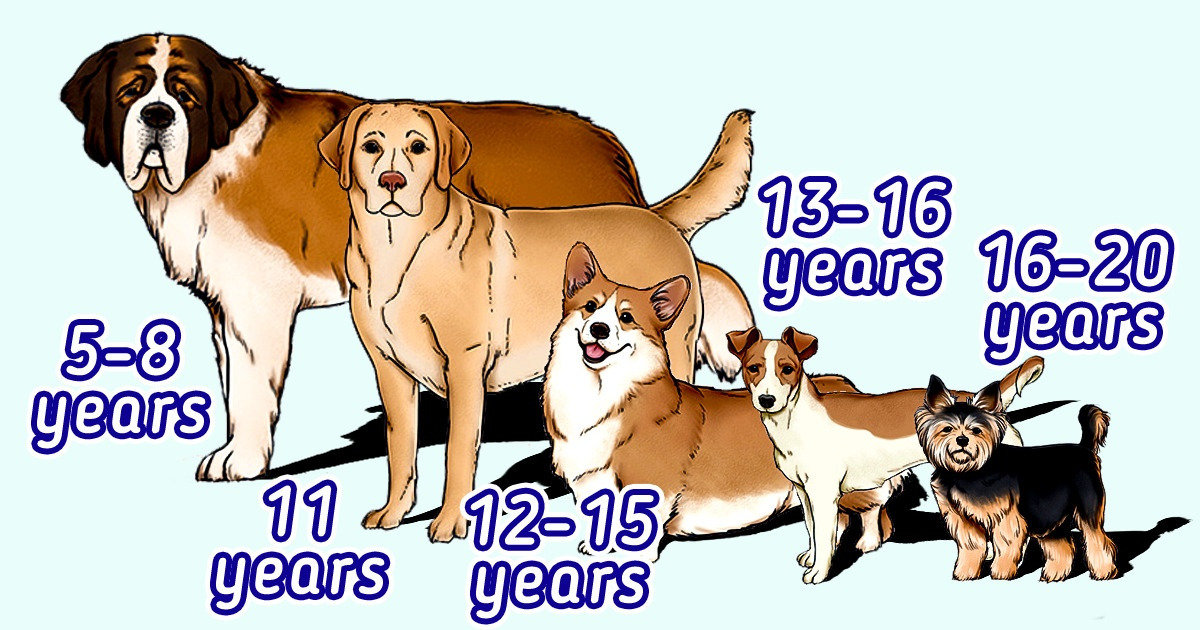
A much-loved dog becomes a family member. But when getting a 4-legged friend, you should take many factors into account, including the life expectancy of your chosen breed. Because some breeds live less than 10 years, while others can live for as long as 20 years.
5-Minute Crafts would like to tell you about the average life expectancy of different dog breeds.
It’s impossible to say for sure how long a dog will live but there is data on their average life expectancy. Also, it’s worth mentioning that breed isn’t always the most important thing in this matter. Different factors affect the life expectancy of your pet.
Lifestyle

Every owner knows that a dog needs quite a lot of attention. Animals need to be able to get enough physical activity. They need to be taken for a walk every day so that they release energy and warm up. For dogs, there are special areas where they can run, jump, and so on. Many people also take their pets to classes at special clubs. It all depends on your personal preferences.
In addition to physical activity, a 4-legged friend should also have mental stimulation. It is good for them to learn commands and just play. Dogs really appreciate attention from their owners and they love spending time together with them.
Health

If you want your dog to live a long life, you need to monitor its health, take it to routine check-ups, and get regular vaccinations and other procedures. If your pet has chronic diseases, keep them under control and follow all of the doctor’s recommendations.
Different dog breeds are predisposed to certain diseases. Study them and their symptoms so that if they appear, you know to seek help immediately.
Remember that dogs, just like people, need to visit the dentist. They can develop periodontal disease, which leads to inflammation of the gums and loss of teeth.
Hygiene

It is important to not forget about hygiene. If you don’t follow basic rules, this can lead to the growth of bacteria on your pet’s dishes, as well as on other surfaces in your home.
- Thoroughly wash the paws and other dirty areas on the pet’s body after a walk. Make sure that nothing is clogged between the pads of the paws and under the claws.
- Bathe your dog thoroughly, as often as the breed and coat require.
- Regularly brush a pet that has long or medium-length hair.
- Keep an eye on the ears and eyes of the animal and don’t forget to clean them.
- Monitor the condition of your pet’s teeth. You can brush your dog’s teeth with a special toothpaste. Follow the dentist’s recommendations for this.
- Keep your pet’s bowls clean by washing them daily.
- Wash and disinfect pet toys. The main thing is to use gentle detergents that don’t cause allergies.
- Don’t forget to wash your dog’s clothes, towel, and bed.
Nutrition

It doesn’t matter if you buy your dog food or make it yourself, the main thing is to provide it with a healthy and balanced diet. The animal should consume proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and microelements necessary for an active life. Talk to your vet about this and follow their advice.
Make sure that the dog doesn’t overeat, because excess weight can shorten its life. Provide your pet with constant access to clean drinking water — a dog can’t live without water.
Which dogs live longer
In wild nature, small animals and insects live a short life, while large ones live much longer. For example, on average, a housefly lives for a month, a rat lives 2-3 years, a horse can live up to 30 years, and an African elephant lives up to 70. This means that the size of animals and insects correlates with their life expectancy. But it’s different with dogs.
In most cases, small dogs live longer than large ones. There is no exact answer to the question of why this happens, but some experts believe that age-related diseases develop in large dogs earlier than in small ones.
- Small dogs live 10–15 years, and some breeds live up to 18 years or more.
- Medium-sized dogs live 10–13 years, but some breeds live longer.
- Large dogs live 8–12 years.
Remember that these are only average numbers. More accurate information can be found in the description of the breed.
Mixed-breeds tend to live longer than purebred dogs. This is because they have stronger immune systems and are less likely to get sick.
Life expectancy of popular dog breeds
Average life expectancy of the most popular dog breeds is:
- Labrador Retriever — 11 years
- German Shepherd — 11 years
- Golden Retriever — 11 years
- French Bulldog — 8–10 years
- Bulldog — 8–12 years
- Beagle — 12–15 years
- Poodle — 12 years
- Rottweiler — 9 years
- German Shorthaired Pointer — 12–14 years
- Boxer — 9–10 years
- Siberian Husky — 12–15 years
- Great Dane — 6–8 years
- Pembroke Welsh Corgi — 12–15 years
- Doberman Pinscher — 10–13 years
- Australian Shepherd — 12–18 years
- Miniature Schnauzer — 12–14 years
- Cavalier King Charles Spaniel — 9–14 years
- Shih Tzu — 12–16 years
- Boston Terrier — 11–15 years
- Havanese — 14–16 years
- Shetland Sheepdog — 12–13 years
- Bernese Mountain Dogs — 6–8 years
- Pug — 12–15 years
- Russian Toy — 10–15 years
Breeds with a short life expectancy

The life expectancy of dog breeds that live fewer years than other breeds (average numbers):
- French Mastiff — 5–8 years
- Great Dane — 6–8 years
- Bernese Mountain Dog — 6–8 years
- Irish Wolfhound — 6–10 years
- Neapolitan Mastiff — 7–9 years
- Leonberger — 8–9 years
- Newfoundland — 8–10 years
- Saint Bernard — 8–10 years
- Scottish Deerhound — 8–10 years
- Bloodhound — 9–11 years
10 of the longest living dog breeds

- Mediterranean Maltese — 12–15 years
- Jack Russell Terrier — 13–16 years
- Yorkshire Terrier — 16–20 years
- Toy Poodle — 14–20 years
- Cockapoo — 12–18 years
- Scottish Collie — 12–16 years
- Lhasa Apso — 14–20 years
- Pomeranian — 12–16 years
- Dachshund — 14–20 years
- Chihuahua — 14–20 years
These are also average numbers.
Common signs of aging in dogs

There are signs that indicate when a pet is aging. By noticing them in time, you can smoothly switch to the appropriate care for your 4-legged friend.
- Eyes. As dogs age, their eyesight deteriorates and their eyes can become cloudy.
- Frequent urination. Elderly dogs often have kidney problems that lead to frequent urination.
- Behavior change. The dog’s character may change, which generally includes a short-tempered nature, dementia, and confusion.
- Difficulty getting up. Older dogs may develop arthritis or hip dysplasia, making it difficult for them to get up.
- Weight change. As dogs age, their metabolic rate changes and thyroid problems can also develop. Because of this, dogs often gain or lose weight.
- Lethargy. Elderly dogs become increasingly lethargic. They often don’t want to play and run like they used to.
- Sleepiness. Elderly dogs sleep more and deeper.
- Fatty lumps. As dogs age, fatty lumps called lipomas may appear on their skin. These are benign and painless tumors.