What’s the Difference Between a Wolf and a Coyote?
Wolves and coyotes share many similarities, but you can distinguish them by many features, including their size and the shape of their snout. You can also tell a wolf from a coyote by their habitats in some cases.
5-Minute Crafts will now explain, in detail, what the key differences between a wolf and a coyote are.
1. Check the size and weight.
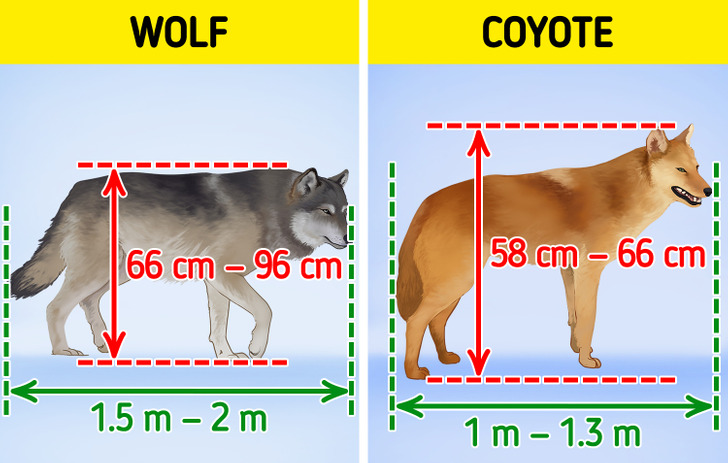
One of the main differences between wolves and coyotes is their size.
- Full-grown wolves are bigger than adult coyotes, usually somewhere between 26 inches to 38 inches (66 cm to 96 cm) tall and 4.5 ft to 6.5 ft (approximately 1.5 m to 2 m) long. Furthermore, the Arabian gray wolf weighs around 45 lb (20 kg), while the Northwestern wolf can weigh up to 175 lb (80 kg). Thus, an adult wolf usually appears as a large-sized dog to human eyes.
- Full-size coyotes are typically between 23 inches to 26 inches (58 cm to 66 cm) tall and between 3.3 ft to 4.3 ft (1 m to 1.3 m) long. Consequentially, they are significantly lighter than wolves, weighing anywhere from 20 lb to 40 lb (9 kg to 18 kg). Hence, a full-grown coyote appears like a mid-sized dog to humans.
2. Check the fur color.
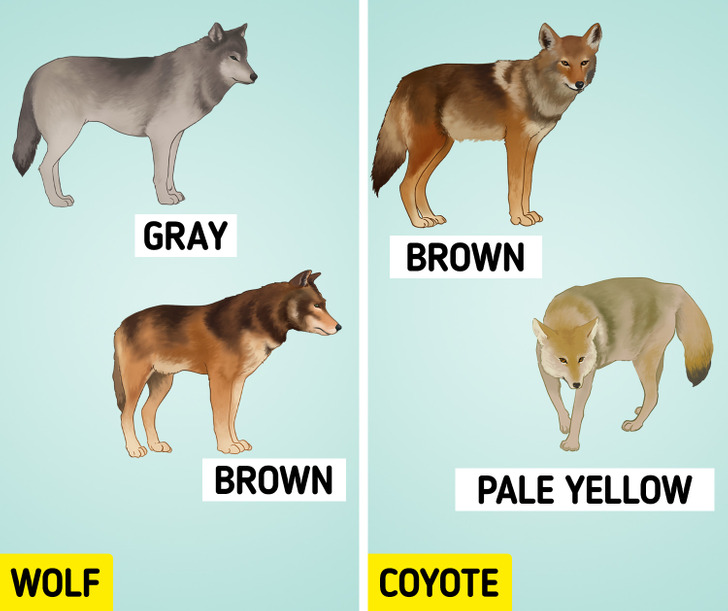
You can also differentiate a wolf from a coyote by the color of the coat.
- In most cases, wolves tend to be gray, dark gray, and reddish-brown. Furthermore, black wolves are relatively common, while white-colored wolves are rare. Also, red wolves may feature occasional white or yellow patches, mostly around their faces, legs, and chests.
- Coyotes’ fur is usually brown and pale yellow. Black and white coyotes can also be spotted, but this is rare.
3. Note their faces.
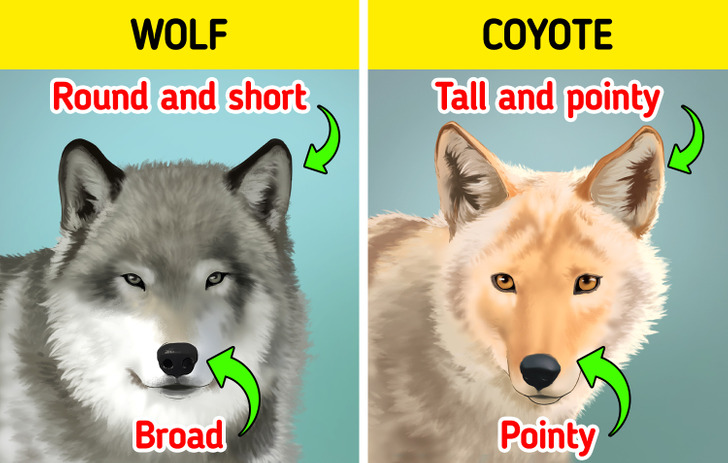
You can accurately tell a wolf from a coyote by the shape of their face.
- The face of a wolf is wider than a coyote’s. Consequentially, wolves have broader noses. Finally, their ears are rounded and shorter compared to coyotes.
- A coyote’s face is slender compared to a wolf’s. Accordingly, their snouts are more angular and slender. Moreover, a coyote boasts tall and pointy ears.
4. Pay attention to the sounds they make.

Given that you hear but don’t see them, you can still figure out whether you’re hearing coyotes or wolves by the sound of their howls and barks.
- Wolf howls are low-pitched and long, in general. Additionally, wolves bark and growl. They also tend to whimper when greeting each other.
- In contrast, coyotes have high-pitched howls that tend to be punctuated by barks, yips, yelps, and yodels. In general, these sounds might remind you of a pack of playful terriers. Also, the range of their howls from low to high-pitched might seem like a human laugh or scream.
5. Measure their paw size.

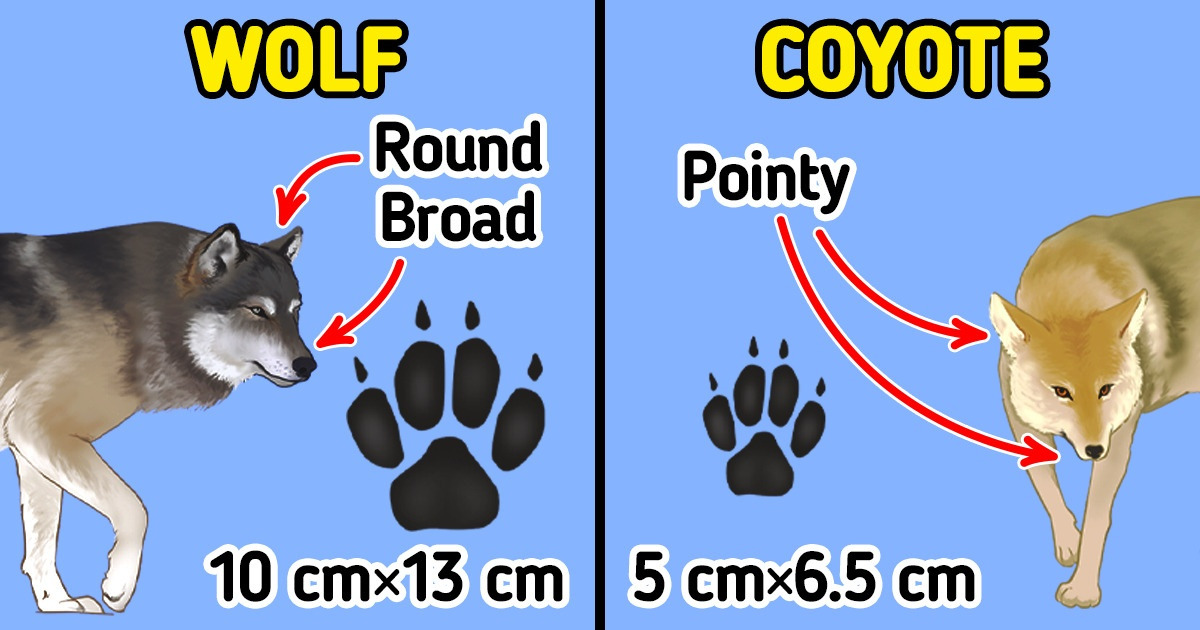
If you find trails of one of these animals, you can identify whether they belong to a wolf or a coyote by the paw size.
- Tracks of an adult wolf are bigger, measuring 4 inches in width and 5 inches in length (10 centimeters in width and 13 centimeters in length).
- The paw of a grown-up coyote is 2 inches wide and 2.5 inches long (approximately 5 centimeters wide and 6.5 centimeters long).
6. Know where they live.
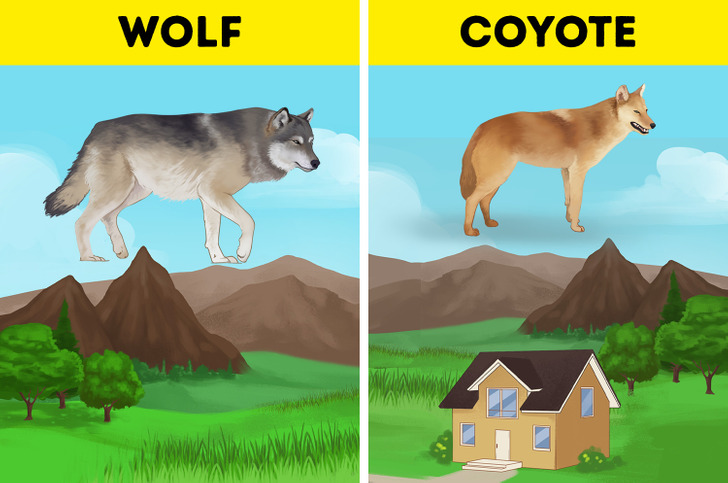
Coyotes and wolves live in diverse habitats, and wolves are more restrictive regarding encounters with humans.
- Wolves inhabit forests and mountains. They also live in open spaces, and gray wolves, for example, inhabit tundras, marshlands, and lowlands. Finally, wolves typically avoid contact with humans by staying away from settlements.
- Coyotes live in forests and meadows, but they also inhabit desert lands and mountains. Moreover, coyotes have adapted to living near human settlements thanks to a constant food supply.
7. Learn their diet.
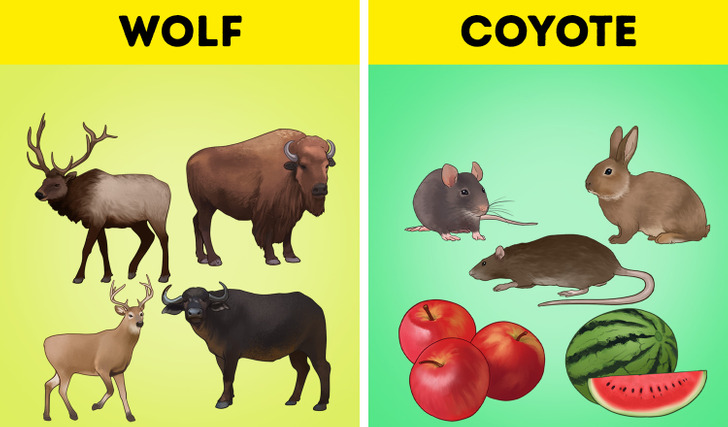
Both coyotes and wolves are meat-eaters, but they still have different diets.
- Wolves live only on meat. They hunt large animals, such as deer, buffalo, elk, bison, and moose. Wolves also eat smaller animals, such as hares, beavers, and various rodents.
- Unlike wolves, coyotes feed on small animals, such as mice, rats, and rabbits. Also, they could become vegetarians and eat fruits (watermelon and apples, for example) and grass in times of crisis.