How Muscles Grow
5-Minute Crafts found out about how muscles work and why they grow.
How muscles work
There are 3 main kinds of muscles:
- Smooth — which are located in internal structures of the body, such as intestines, blood vessels, and others. They are involuntary muscles because their motion happens without our conscious awareness.
- Cardiac — these are involuntary striated muscles, the main tissue of the heart.
- Skeletal — these are striated muscles attached to the bones that allow movement.
Interestingly, all kinds of muscles share the same composition, even though their functions are different. Every muscle consists of elastic tissue which, in turn, is made from tens of thousands of fibers.
The neuromuscular system (consisting of skeletal muscles, brain, and nerves) is activated to make mechanic movement. On average, every muscle has 50-200 motor neurons. The brain sends them a signal, triggering a reaction that leads to contraction and motion.
Aside from allowing movement, muscles have other functions:
- Making bones stronger and protecting your joints
- Increasing the speed of metabolism
- Keeping you in shape
- Making your everyday activity easier
- Lowering the risk of disease
The difference between male and female muscles

According to scientists, the difference between male and female muscles is the fiber composition, contraction speed, and energy metabolism. In most cases, male muscles have a higher capacity for anaerobic metabolism — a creation of energy due to the combustion of carbs without oxygen. Female muscles are more fatigue-resistant and can recover faster.
It’s not completely clear how sex determines the characteristics of muscles. It’s probably due to hormones.
How muscles grow
In short, this is how we can describe the system of muscle growth. During workouts, the cellular proteins in the muscles are damaged. It activates the cellular process that restores the muscle fiber, making it grow.
In fact, it’s a far more complicated molecular biology process. It occurs when the muscle protein is synthesized faster than it breaks down.
Basically, muscle growth is the body’s biological attempt to restore or replace muscle fiber that was damaged as a result of intense workouts. Thanks to the merging of satellite cells (inside the muscle fibers) and the muscle fibers, the cross-sectional area of muscles increases and muscle hypertrophy occurs.
During workouts, the anterior pituitary gland releases the growth hormone. The more intense a workout is, the more the hormone is produced. This hormone activates the process of turning fats into energy needed for growth and delivers the amino acids to the protein of skeletal muscles.
Insulin also plays its role. It stimulates muscle tissue growth, increasing protein synthesis and simplifying the entry of glucose into the cells, which is used as energy for cell growth.
What influences muscle growth
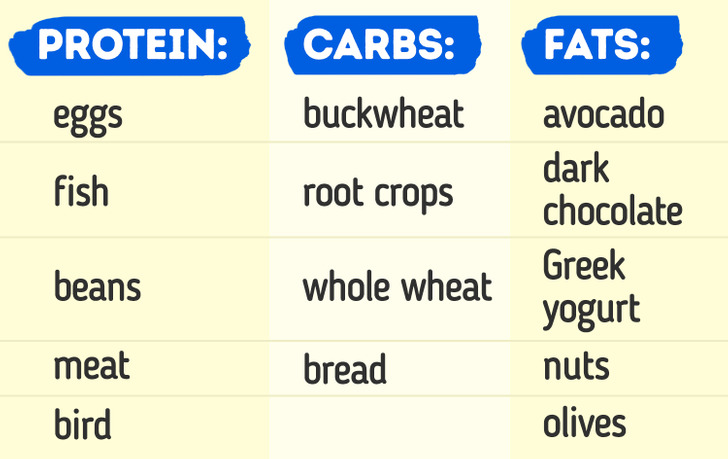
According to studies, to make your muscles grow, you need to eat protein from 1.6 to 2.2 grams/1 kg of body weight every day, along with your workouts.
You should also eat carbs and fats if you want to increase your muscle mass.
The body also needs glucose, minerals, electrolytes, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, and other nutrients.
Another important factor is sleeping well. Sleep deprivation slows down protein synthesis and prevents the muscles from restoring after physical activity, which leads to a decrease in muscle mass.