How Our World Formed, and What the Multiverse Is
Have you ever thought about how our world appeared? There are different models of our universe’s evolution, but the most renowned one is called the Big Bang Theory.
At 5-Minute Crafts, we want to explain in simple terms what this theory is so that even a child could understand how our universe was formed.
What the Big Bang Theory is
In 1927, Belgian astronomer Georges Lemaître suggested that our entire universe once originated from a single point, and after that, it expanded to its current state. 2 years later, his colleague, American astronomer Edwin Hubble, discovered that all observable galaxies were moving away from us. And the farther away the galaxy was from the Milky Way (the galaxy where we live), the faster it was moving away from us. This confirmed Lemaître’s assumptions, and scientists began to develop this theory, or rather, the model for our universe’s evolution.
- The term “Big Bang” appeared later. It was first used by British astronomer Fred Hoyle during a radio broadcast in 1949.
Today, we say that, from the scientific point of view, the Big Bang theory is a model of the origin and evolution of our universe. The name suggests that it all started with an explosion, but this is not so.

According to the Big Bang Theory, our universe was once smaller than an atom. All the matter in the universe was held in a tiny point, which had a huge mass and a very high temperature. This state is called the initial singularity.
It’s assumed that approximately 13.7 billion years ago, the universe contained in this point didn’t explode, but began to expand rapidly. This is what we call the Big Bang. As the universe grew, it also cooled. So gradually and slowly, the world familiar to us was formed. Let’s look at the main events that happened in our universe after the Big Bang.
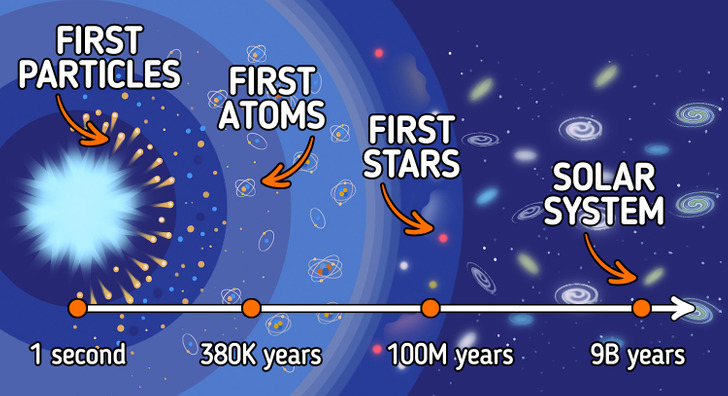
- In the very first seconds of the universe’s existence, particles of matter and antimatter were formed. And the result of the collision of these particles and antiparticles were protons and neutrons. These are elementary particles that make up the nuclei of atoms.
- A few minutes after the universe appeared, its temperature dropped to 1.8 billion°F. This was enough for neutrons and protons to form hydrogen and helium nuclei.
- After 380,000 years, the temperature of the universe cooled to 4,940°F. Thanks to this, protons and electrons could combine to form the first atoms, and the universe was filled with huge clouds of hydrogen and helium. Space became transparent, but darkness still reigned everywhere.
- 100-200 million years passed after the Big Bang before the first stars began to form, gradually forming galaxies.
- 9 billion years after the Big Bang, our solar system was formed from a molecular cloud of gas and dust, and about 100 million years later, the Earth was formed. A little less than 1 billion years later, life emerged on it.
- 13.7 billion years after the Big Bang, the first recognizable humans emerged on Earth. This happened quite recently, about 2 million years ago.
What will happen to the universe in the future
Today, the temperature of the universe is −455°F, and its size is so large that we’re unable to physically observe it, even using the most advanced astronomical instruments.
What will happen to it in the future? There is an opinion that the universe will continue to expand until it stops, and after that, it will begin to shrink. Getting smaller and smaller, it will again reach the point of singularity, and then, perhaps, a new, different universe will begin to expand.
If there are any other universes
There is a myth that the Big Bang theory explains the origin of the universe. But, as you can see, this is not so, as this concept only suggests a possible beginning and describes the evolution of our current universe from a single point. This model of the universe’s evolution is quite new, and scientists continue to work on it.
For example, there are some people who believe that the moment the universe began to expand was the beginning of time. Other scientists suggest that this is not so and that different universes can exist simultaneously. Moreover, they bump into each other causing Big Bangs, due to which an infinite number of universes are formed, coexisting in a single Multiverse.
Some scientists claim that there is a mirror universe to our own. In this universe, the starting point is also the point of singularity, but time flows in the opposite direction.
