Why Humans and Animals Don’t Grow Permanent Teeth From Birth
Children get really excited when losing a tooth. But one can’t say this about adults — it’s hard to imagine that anyone would be happy about losing a tooth at an older age. Many of you have likely wondered why we grow our milk teeth first followed by our permanent teeth a few years later.
5-Minute Crafts would like to tell you about why humans and many animals don’t grow permanent teeth from birth.
Why we need teeth

Teeth are bony structures in the mouth. They are the hardest part of the human body. Some people think teeth are bones. However, this is not true, although there are similarities. Their main difference is in regeneration. A damaged bone is able to repair itself, and a tooth is not.
Teeth are a very important part of the human body. They perform important functions.
- Speech: When we speak, our teeth interact with our tongue and lips to help us pronounce different sounds. Without teeth, we would still be able to speak, but not so easily.
- Maintaining bone structure: When we chew food with our teeth, the jawbone becomes stronger. Without chewing, this bone will become smaller and thinner. The bones of the jaw support the muscles responsible for facial expressions. Without them, our face would change significantly: the upper lip would become longer, the muscles would lose tone, and the vertical lines of the face would become deeper.
- Smiling: Of course, you can smile without teeth, but many people don’t want to.
- Producing and holding in saliva: Teeth contribute to the production of saliva because chewing stimulates the salivary glands. This releases valuable enzymes that help pre-digest food, making it easier for the gastrointestinal tract to do its job. Besides, teeth serve as an additional barrier that keeps saliva in the mouth.
- Protecting from health problems: Chewing food with the gums can lead to gum disease. Plus, it’s impossible to chew food properly without teeth. Therefore, it will be more difficult for the body to break it down into particles that are easy to digest. And this could lead to nutritional deficiencies, which, in turn, would provoke health problems.
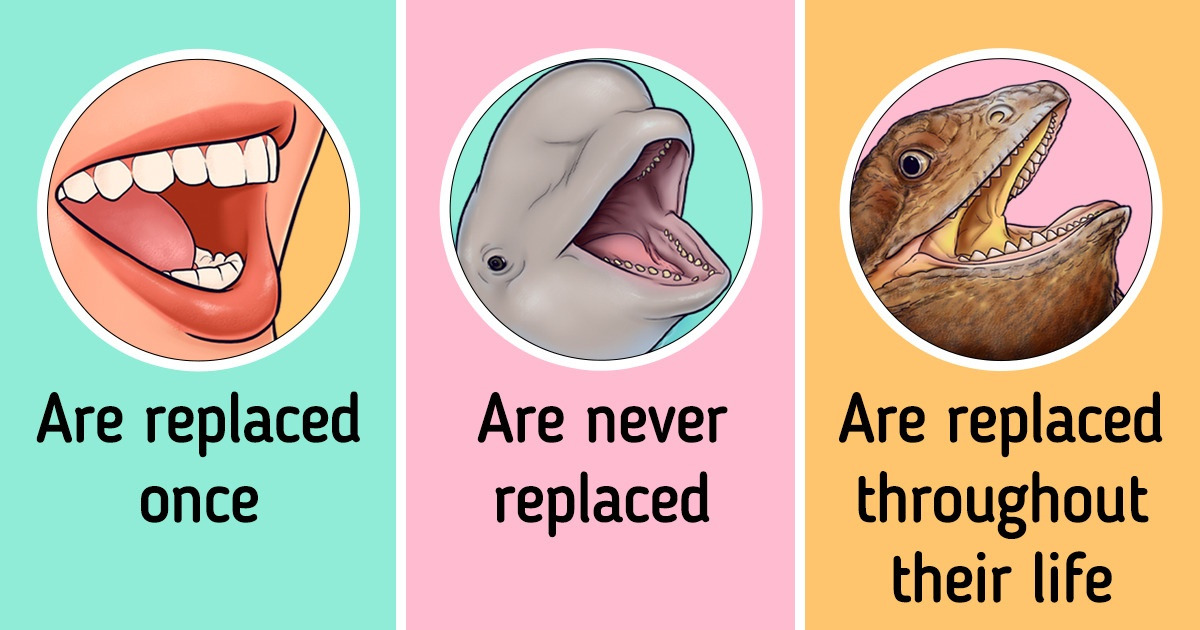
Who diphyodonts, polyphyodonts, and monophyodonts are
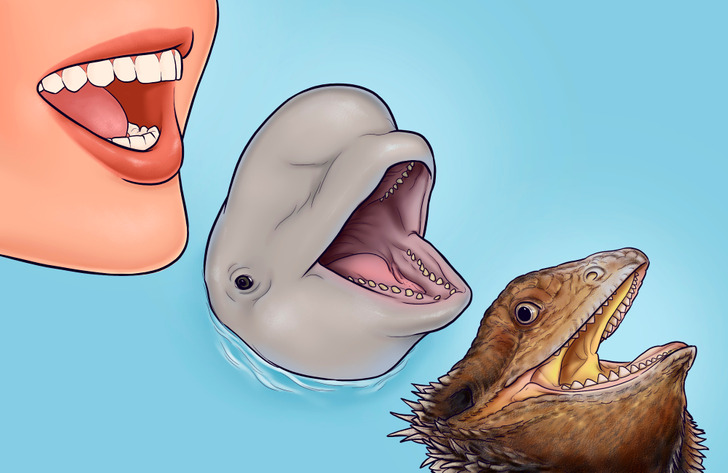

Most mammals, including humans, are diphyodonts. Diphyodonts are animals with 2 successive sets of teeth: milk teeth and permanent teeth. This means that first, they grow milk teeth, and then they are replaced by permanent teeth. But there are 2 other types of animals with different types of teeth.
- Monophyodonts: They have one set of teeth for their entire life. The beluga whale, for example, grows only one set of teeth that are never replaced.
- Polyphyodonts: Their teeth are replaced regularly. The teeth of sharks, frogs, and iguanas, for example, are constantly replaced throughout their life.
But this is not the only classification of animals by teeth.
- Homodonts are animals whose teeth are all the same, like sharks, dolphins, and beluga whales.
- Heterodonts are animals that have different teeth. Heterodonts include most mammals and humans.
Human permanent teeth are divided into 4 classes:
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Thus, a person can be classified as heterodont and diphyodont. This means their teeth are replaced once and have a different shape.
Why teeth are replaced
Humans and many other mammals have their teeth replaced once, from milk to permanent teeth. Some people wonder why we need milk teeth at all and why we can’t grow permanent teeth right away. There is an explanation for this.
First, a person has only 20 milk teeth and 32 permanent teeth. Second, milk teeth are smaller than permanent teeth. Human milk teeth begin to grow at 6 months. At this age, the skull is small and still has to grow and develop. The jaw of a baby is not large enough to accommodate the number and size of adult teeth.
At the same time, milk teeth are not strong enough to be used for the entire life. When our skull is formed and reaches its adult size, milk teeth will be too small and far apart for an adult jaw. These teeth won’t be able to chew effectively. And we have already mentioned above why this is important.
The importance of milk teeth
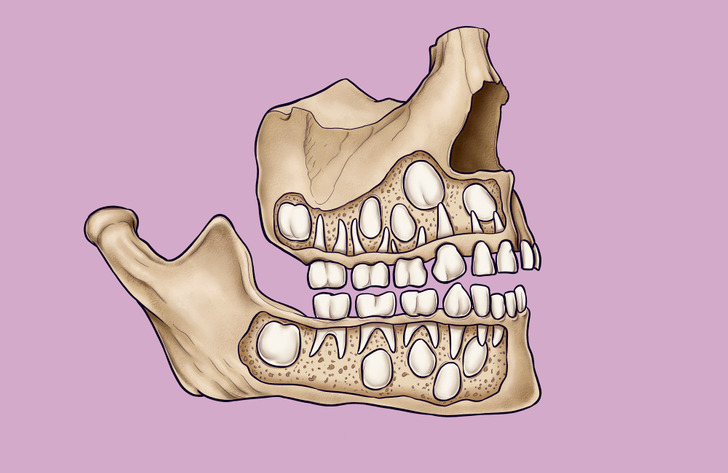
Milk teeth are essential for proper chewing and speech development. But they also have other important functions.
- Milk teeth keep space available so that permanent teeth can erupt normally.
- They distribute forces into the jaws during chewing, which contributes to their development.
- Thanks to the milk teeth, the permanent teeth erupt in a more organized manner.
Consequences of early loss of milk teeth:
- If a baby tooth has to be removed early, some of the space needed for adult teeth in the dental arch can be lost. This can cause permanent teeth to become crowded.
- Sometimes the early loss of milk teeth can delay the eruption of permanent teeth.