How to Choose a Bicycle
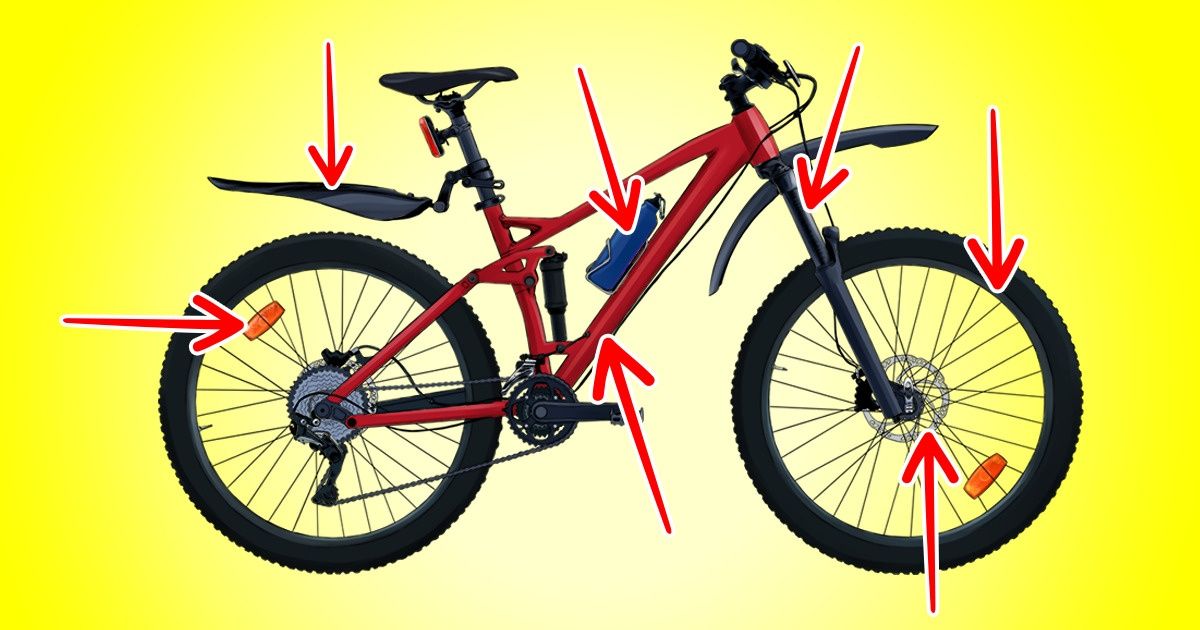

When trying to choose the right bicycle, think about the following questions: which route will you take and which roads will you be taking on it? Depending on the answer, you’ll be able to opt for the most suitable option, especially considering the fact that today’s assortment is quite vast. Also, keep additional elements in mind that your new purchase may be equipped with.
5-Minute Crafts will help you decide on the size of your bicycle and pick the best model depending on the types of rides you plan to take.
Types of bikes

-
Road bikes are meant for quick rides on smooth, asphalt roads. They have narrow wheels and drop-shaped handlebars. They are usually lighter than other types of bicycles. They can be ridden on paved trails but will likely be uncomfortable and unstable on unpaved trails. Most road bikes don’t stand heavy loads, which is why they are not suitable for rides to work or traveling.
-
Mountain Bikes (MTB) are designed to be ridden on roadless trails. They don’t have a big gear range but the amount is enough for driving on off-road trails. Most mountain bikes have one of 2 types of amortization. “Hardtails” are the models that have only front suspension. If a bike has both front and rare suspensions, it’s called a “full-suspension bike” or “dually.” If a bike has no amortization, it means you are dealing with a “rigid.” Powerful bikes with wide tires are a part of the MTB category.
-
Hybrid bikes have big soft saddles and upright handlebars that provide a comfortable riding position. They usually have medium-width tires with a semi-smooth tread to provide a fairly smooth ride on pavement and enough grip on unpaved trails. However, they won’t be appropriate for off-road riding. Most hybrid bikes have a front suspension, but one can find rigid too.

- City bikes are a good choice for those who plan to ride around the city. There can be many variants, but their construction is typically the same. They provide the upright riding position of the rider, which helps them to see far distances and observe things around them better. They often come with one gear only and have no gear shifters. City bikes usually come with a rack, mudguards, fenders, chain guards, skirt guards, and lights already mounted.
- BMX (Bicycle Moto Xtreme) are popular among those who like extreme riding and performing tricks. They are not used for everyday needs. The characteristics of these bikes are small wheels, tall handlebars, a low saddle, and a small frame.
💡 Apart from the aforementioned types of bicycles, there are many others, but they’re not as popular and have specific characteristics.
Picking the right bike for your size

Method #1. Swing your leg over the frame and stand over it. Check how far the distance between your body and the frame is. Ideally, there should be about 1-1.2 inches if you’re looking for a road or hybrid type of bike, and 2 inches if you’re going for a mountain bike.
💡 If you’re buying a bike online, you obviously won’t have a chance to check the size with the help of this method. In this case, you’ll have to rely on the measurements of your body to make the choice.
Method # 2. Measure the length of your inseam, the distance from the crotch to the heel. When all the measurements are done, find the length of the frame you need by making these simple calculations:
- For a road bike — an inseam of × 0.7
- For a mountain bike — an inseam of × 0.66
- For a hybrid bike — an inseam × 0.69
It means that if your inseam is 30 inches, the size of the frame should be 20.8, 19.7, or 20.5 inches, respectively.
💡 Ignoring these calculations increases the risk of experiencing trauma while riding. The absence of the space between the frame and your body can lead to a hit if you have to stop suddenly.
Characteristics that affect the cost
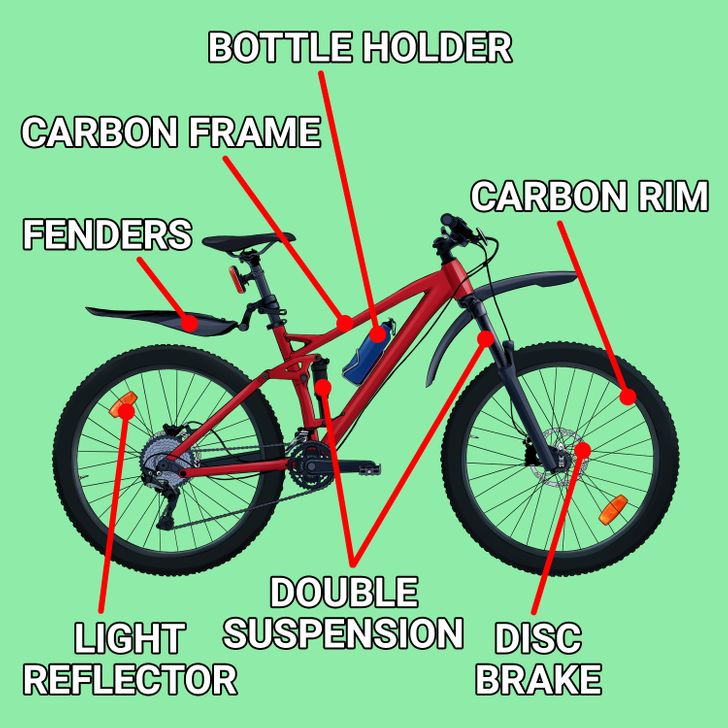
You don’t need to analyze each technical element to choose a more suitable bicycle. However, some functions and prime characteristics can increase its cost. When calculating your budget, take into account the following components that will affect the price.
- Full suspension, hardtail, or the absence of the suspension: Duallies that have amortization on both wheels usually cost more. At the same time, they provide a smoother ride and help to overcome hard-to-ride parts of trails. The stiff rear part of hardtails, which has suspension in the front part only, does absorb hits but much weaker.
- Materials made of carbon, aluminum, steel, or titanium: Carbon frames can be very stiff while remaining light at the same time. Thanks to the flexibility of the material, the construction is quite aerodynamic. In terms of strength and lightness, aluminum is inferior, but in recent years, production technology has progressed and a good aluminum frame often outperforms a cheap carbon one. Steel frames are heavy but provide comfort on long rides thanks to their springs. Titanium is lighter, stiffer, and more long-lasting than other materials, but it costs quite a lot. Oftentimes it’s even combined with aluminum.
- Wheels: They depend on what type of bike you choose. Pay attention to rims. Most of them are made of aluminum. This material supplanted steel a few decades ago, as it’s lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant, and provides excellent braking performance. Recently, carbon has become more common in rims of road and mountain bikes, but it’s quite expensive.
- Brakes: In previous years, rim brakes used to be the norm, while disc brakes were an exception. However, the latter has excellent stopping power irrelative to conditions and are now dominant on the market. Rim brakes squeeze pads on the sides of the rims. They still remain a budget-friendly option. Disc brakes capture the brake rotor installed on the wheel hub. There are hydraulic and mechanical disc brakes — the former self-adjust during wear, and the latter must be adjusted manually.
- Additional elements: Fenders, light reflectors, and a bottle holder are useful additional elements that will make your bike more practical. They are often forgotten about, but in some cases, they are more important than having the opportunity to shift gears.