False Facts About Coffee We Continue to Believe In
Though millions of people around the world can no longer imagine their lives without a cup of morning coffee, many of us still mistrust this drink, all because it causes addiction, provokes insomnia, and affects a person’s growth — as rumor has it, anyway.
5-Minute Crafts decided to find out what common facts about coffee are true and which ones are just nonsense.
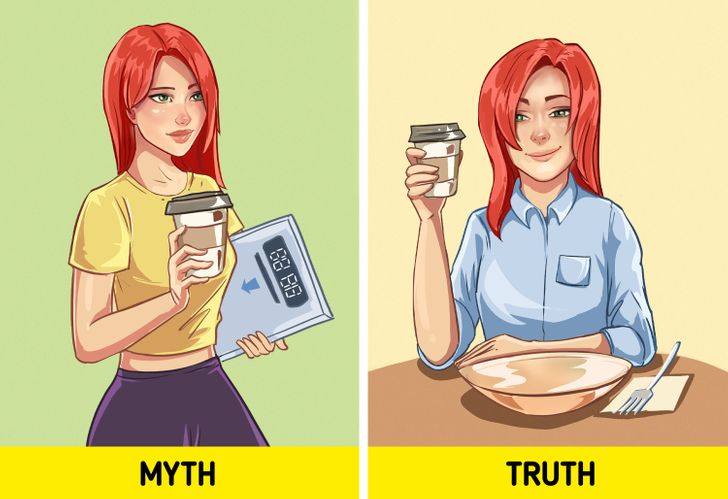
Coffee helps you get slim.
Coffee can stunt your growth.
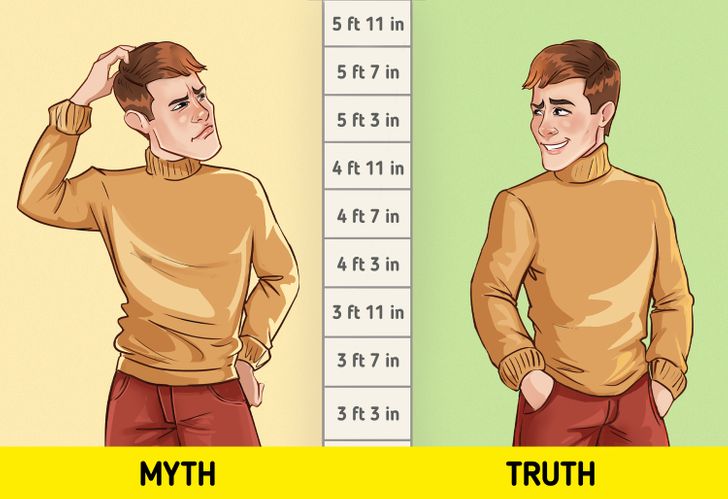
At the moment, there is no scientific evidence that coffee can slow human growth.
Perhaps this myth has appeared due to research where they assumed that fans of coffee were more prone to developing osteoporosis. It has been hypothesized that caffeine can increase the excretion of calcium from the body, thereby increasing the risk of disease. However, it has been found that coffee has only a small effect on calcium excretion, and the link between consuming this drink and osteoporosis has not been confirmed.
It’s also worth noting that osteoporosis affects the fragility of bones but doesn’t affect the height of a person.
Decaffeinated coffee doesn’t contain caffeine.

Experts claim that almost all coffee (even decaffeinated) contains caffeine in bigger or smaller amounts. Of course, the concentration of caffeine in a decaffeinated drink will be much lower, but if you drink 5-10 cups per day, you can easily get the daily dose, which is contained in 1-2 cups of regular coffee.
Coffee causes addiction.
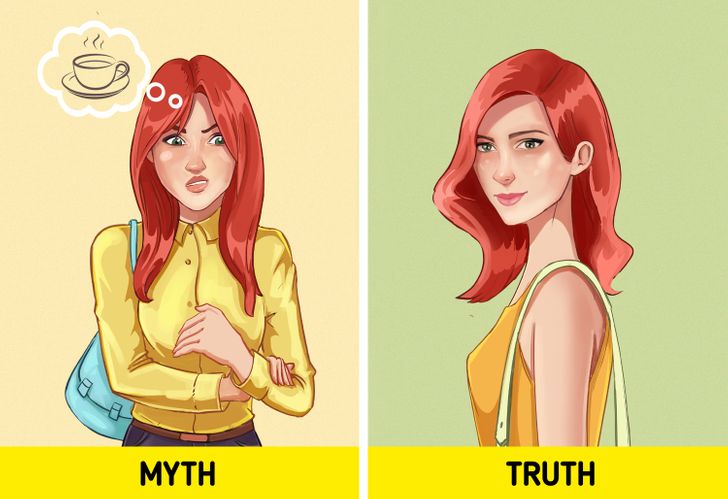
Caffeine is a stimulant of the central nervous system and is indeed mildly addictive when consumed regularly. Despite this, you can easily give up on drinking coffee. In most cases, the sensations caused by a lack of caffeine (fatigue, poor concentration, irritability) subside within a few days. For this reason, experts don’t consider coffee to be an addictive product.
Coffee causes insomnia.
Researchers didn’t find any connection between the amount of consumed coffee and the quality of sleep. This could be proof that coffee itself doesn’t cause insomnia. You can safely drink it in the morning without fearing that it will affect your sleep. But since caffeine has a stimulating effect, you should stop drinking it at least 6 hours before bed.
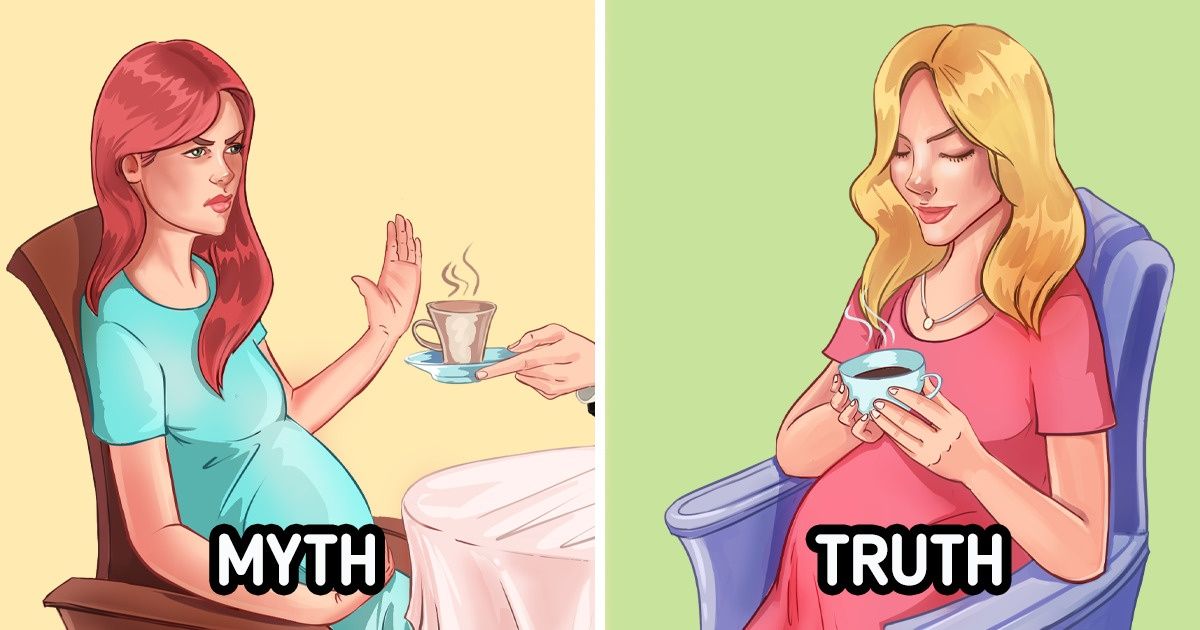
Pregnant women can’t drink coffee.
Though it’s recommended for pregnant women and those who want to have kids to cut back on the amount of coffee they drink, most experts believe that 200 mg of caffeine a day is safe. It equals about 1 big cup of coffee.
However, since the indications and contraindications are often individual, it’s always best to consult your doctor. They will tell you whether you can drink coffee or not and set the recommended daily norm for the drink.
Coffee can cause dehydration.

The myth that coffee can cause dehydration dates back to a 1928 study where the active use of coffee was associated with increased urination. Due to this, it has been suggested that the drink has a diuretic effect. The spread of the idea cemented coffee’s reputation as a dehydrating product.
Over the years, this assumption was refuted, and today scientists are sure that coffee provokes just as much urination as other drinks.
Dark roasted coffee beans have more caffeine.
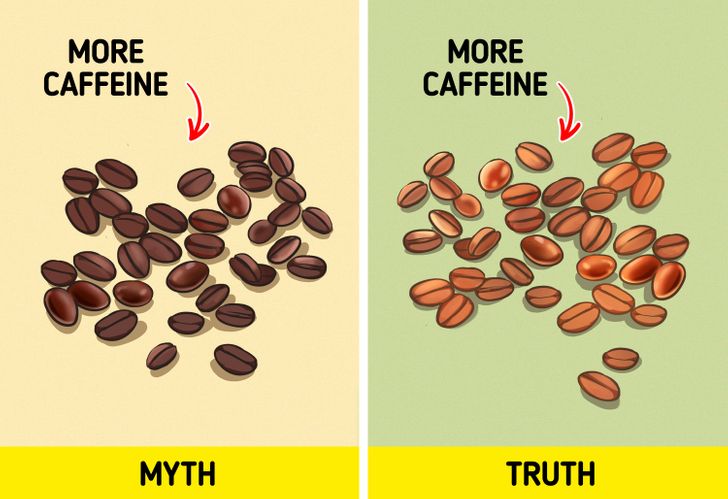

In fact, the concentration of caffeine is more in lightly roasted beans. And though dark roasted beans are often richer and deeper in flavor, this has nothing to do with the amount of caffeine in them.
Coffee is harmful to your health.
Today, scientists are more and more inclined to believe that coffee is healthy provided it’s consumed moderately. Drinking small amounts of coffee is thought to reduce the risks associated with Parkinson’s disease, heart attack, stroke, liver disease, and type 2 diabetes.