The Difference Between a Sentence and a Phrase
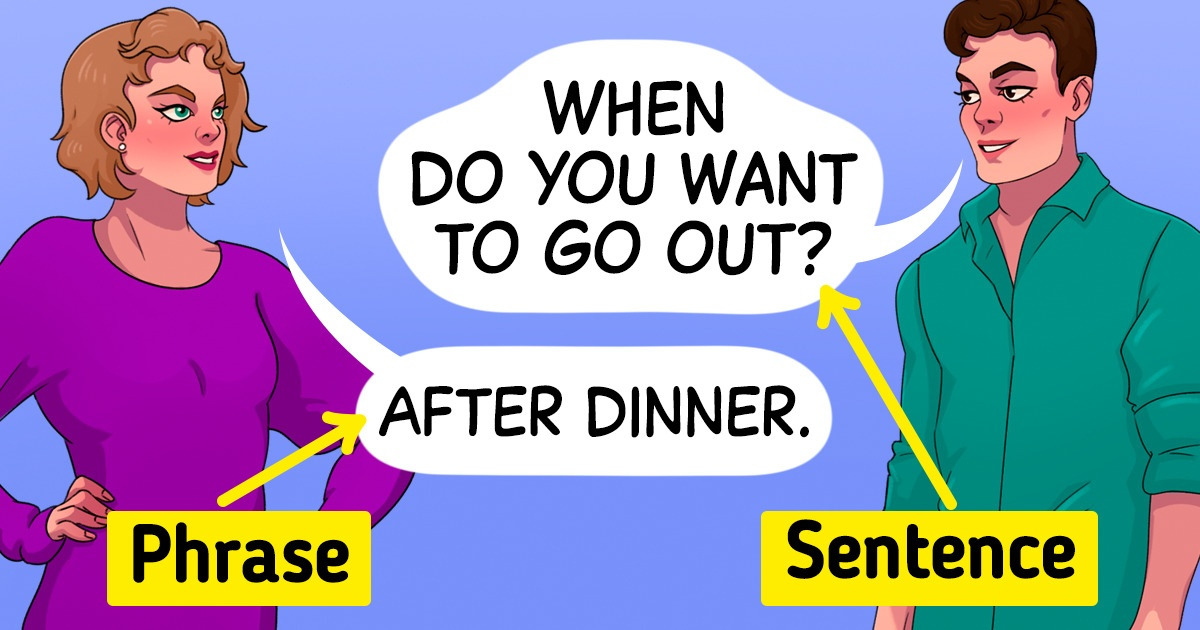
Both native and non-native English speakers use phrases and sentences in common speech since they are commonplace in most languages. That said, we might not always know how to differentiate them — while we know how to use them, we might not know all the rules and names.
5-Minute Crafts will tell you the main differences and categories of these 2 things.
Important to know

- A subject is a person that actually performs the action in a sentence.
For example, in “Maria ate the cake,” Maria is the subject that performed the action, which is eating the cake. - A verb expresses the action performed by the subject.
In the example above, “ate” is the verb, as the action performed by Maria is eating.
What a phrase is
A phrase is a group of words that, although grouped together, don’t contain a complete thought or idea. This means that they can’t be used in writing by themselves since they can lack a subject, a verb, or even both. Therefore, a phrase is like a building block or a single part of a sentence.
Phrases can be long or short: “after lunch” is a phrase, just like “waiting for the rain to stop” is a phrase.
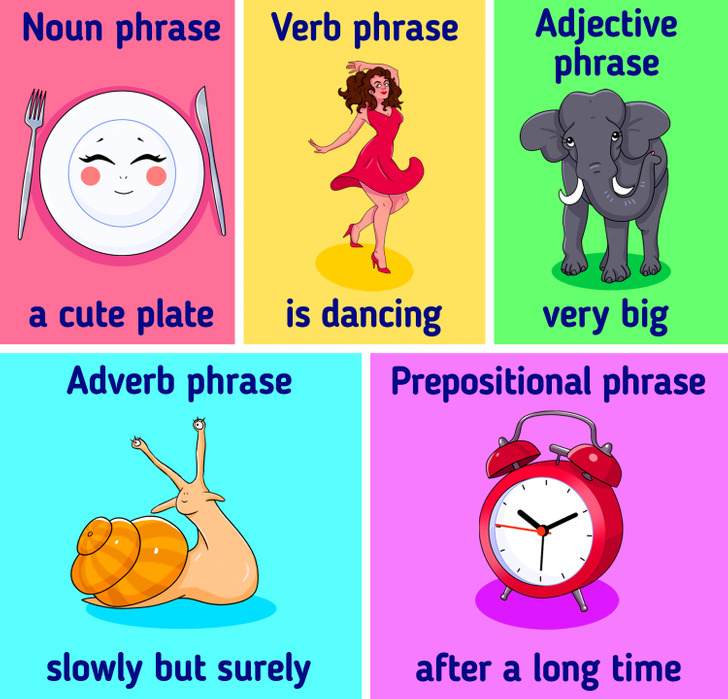
The 5 main types of phrases:
- Noun phrase: “a cute plate”
The word “cute” is giving information and is a modifier to the noun, “plate.” - Verb phrase: “is dancing”
This contains a verb and all related words — “is” connects the verb “dancing” with any subject. - Adjective phrase: “very big”
The word “very” gives information about the adjective, “big.” - Adverb phrase: “slowly but surely”
This phrase works as a single adverb. - Prepositional phrase: “after a long time”
The phrase gives information about subjects and verbs when in a sentence.
What a sentence is
A sentence is a group of words that express a complete thought, which means that, contrary to phrases, they can be used by themselves because they contain both a verb and a subject.
The subject can be present or, in the case of imperative sentences, the subject is who the speaker is addressing.
Sentences can include phrases inside of them.

The 4 main types of sentences:
- Interrogative sentence: “Are you okay?”
They ask a question and have a question mark at the end. - Imperative sentence: “Be quiet! ”
They express orders and instructions. They can be a single word, like “stop!” - Exclamatory sentences: “I won the prize!”
They express surprise or strong opinions and end with exclamation marks. - Declarative sentences: “The book is on the table.”
They give statements and end with a full stop.