10 Things That Happen to Your Body When You Sleep
1. Your body temperature drops.
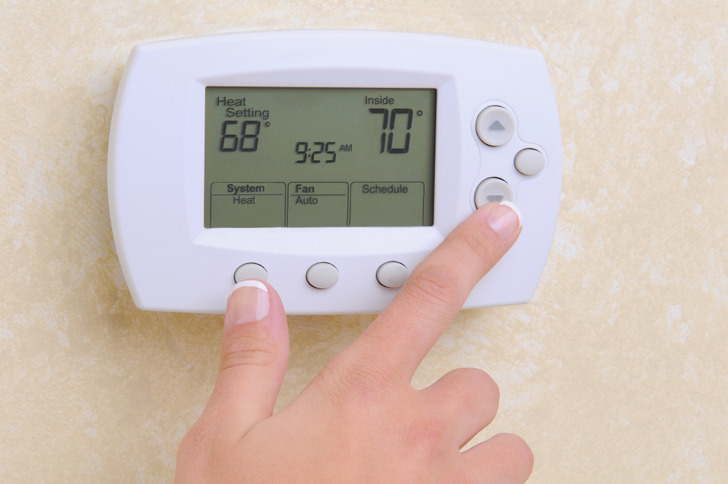

As you get sleepy before going to bed, your body temperature decreases by a couple of degrees, and it reaches its lowest rate about 2 hours before waking up. During REM sleep, your body thermometer is turned off by your brain, which is when the temperature in a room affects you more.
Generally, a cooler room leads to better sleep, while physical exercise, such as push-ups or jogging, increases your body temperature, making you more alert.
2. Your muscles can’t move.

During non-REM sleep, all of our muscles relax and the body’s overall energy expenditure decreases. During the REM phase, the respiratory rate increases and the eyes move actively. During this phase, the body remains motionless. This temporary “paralysis” is needed for our own security. Because of it, we don’t kick, push, or reproduce the actions from our dreams at all.
3. An anti-diuretic hormone turns off your need to pee.

The anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is a hormone that regulates water metabolism in the body. The amount of urine depends on the level of ADH in the body. The higher the hormone level, the less urine the body produces. At night, ADH levels are elevated. This reduces the risk of urination during sleep.
4. Hormones help control weight.

Sleep regulates the concentration of 2 important hormones in our body, ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin controls appetite, while leptin helps control satiety. Sleep restriction can lead to an increase in ghrelin concentration and a decrease in leptin levels. These changes can cause eating disorders and lead to weight gain.
5. Your stress levels drop.

Cortisol is a hormone that helps regulate stress levels in our body. During the first few hours of sleep, cortisol levels decrease. However, closer to the morning, the level of this hormone begins to increase again. This is a natural process, which means that the brain is preparing to wake up in order to activate all the organs in time.
6. Your brain sorts and processes daily information.

During the day, each person is faced with a huge amount of information. During sleep, the brain processes all the information received and moves information from short-term memory to long-term memory. This process helps to consolidate the acquired information for future use. In addition, during the REM stage, the brain gets rid of unnecessary information.
7. Your breathing and heart rate slows down.
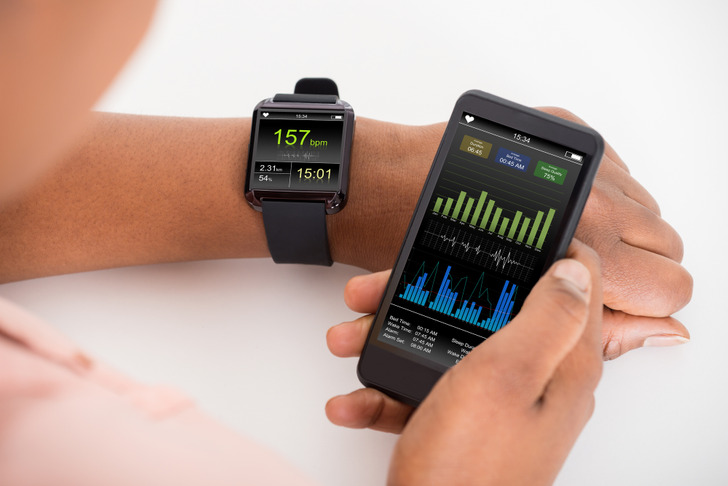

Respiration and heart rate decrease and reach their lowest rate during stage 3, non-REM sleep. When the REM stage occurs, breathing becomes faster and may become irregular. At the same time, the pulse quickens to almost the same frequency as during wakefulness.
8. Your body recovers.
9. You have dreams.

Every night, we dream for about 2 hours. However, we may not remember most of our dreams. Scientists do not fully understand why we dream. Bright events of the day can become part of our dreams. Therefore, if you are worried or stressed, then you may have disturbing dreams. Dreams can be seen in all stages of sleep, but the most vivid dreams occur in the REM phase. Dreams can be either in color or black and white.
10. Your eyes keep moving.
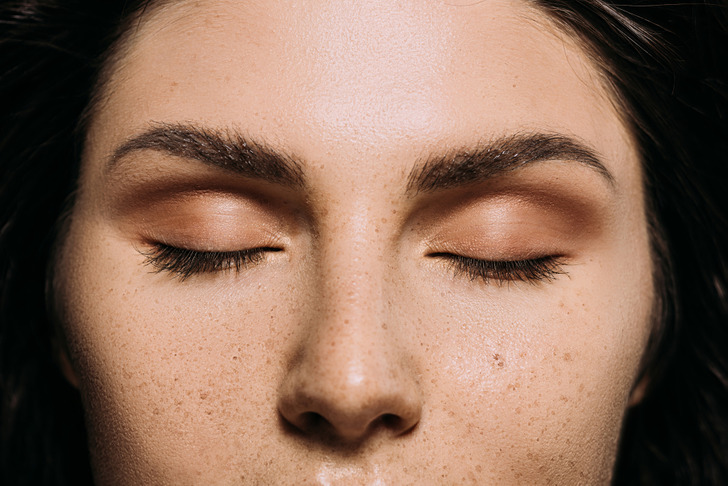

Despite the fact that during sleep our eyes are tightly closed by the eyelids, they continue to move quickly. During non-REM sleep, eye movements are negligible. However, during the REM phase, the eyes can move quite quickly. Scientists do not have an exact answer to the question of why this happens. One belief is that these movements allow us to change scenes in our dreams.