19 Commonly Confused English Words and How to Use Them Right
English has many confusing words that look and sound very similar, which can make them difficult to spell or make it difficult to tell if people are referring to one or the other. We’ve prepared this guide to help you identify the differences between highly used words that may confuse you. Read to find out more.
1. Affect or effect

- Affect (verb): means to influence or cause an effect on something or someone. For example: “Too many hours in the sunlight really affected him. He was very thirsty and tired afterward.”
- Effect (noun): refers to the result or outcome of a specific influence. For example: “Sun exposure can have a tanning effect on your skin, but remember you should always wear sunblock.”
2. Bear or bare
- Bear (verb): means to endure or tolerate something that is usually unpleasant. For example: “I couldn’t bear the suspense. I needed to know what was going on!”
- Bare (adjective): refers to being naked or not covered. For example: “Visitors must take off their shoes and walk into the temple in bare feet.”
3. Breath or breathe
4. Capital or capitol
- Capital (noun): can usually refer to an uppercase letter or a city that serves as a seat of government. For example: “Last summer, I visited Madrid, the capital of Spain.”
- Capitol (noun): a building in which a state legislature meets. For example: “You should walk by the Capitol Building, it’s beautiful.”
5. Dessert or desert

- Dessert (noun): is a sweet food served at the end of a meal. For example: “We will have strawberry cheesecake for dessert.”
- Desert (noun and verb): as a noun, it refers to an area of arid land generally covered with sand, scattered vegetation, and high temperatures. For example: “In some areas of the Atacama Desert, there are no records of rainfall.” As a verb, it means to abandon a place. For example: “They deserted the city because there wasn’t enough water.”
6. Device or devise
- Device (noun): refers to a piece of equipment, an object, or a machine created for a specific purpose. For example: “Turn off your digital devices before starting the test.”
- Devise (verb): means to plan or invent a difficult procedure. For example: “We should devise a system to solve this issue as soon as possible.”
7. Emigrate or immigrate
8. Ensure or insure
- Ensure (verb): means to make sure or certain that something occurs. For example: “We need to ensure that the new products will be in the store on Friday.”
- Insure (verb): means to protect something or someone against risks in case of damage, losses, injury, etc. For example: “Their house was insured immediately after buying it.”
9. Envelop or envelope
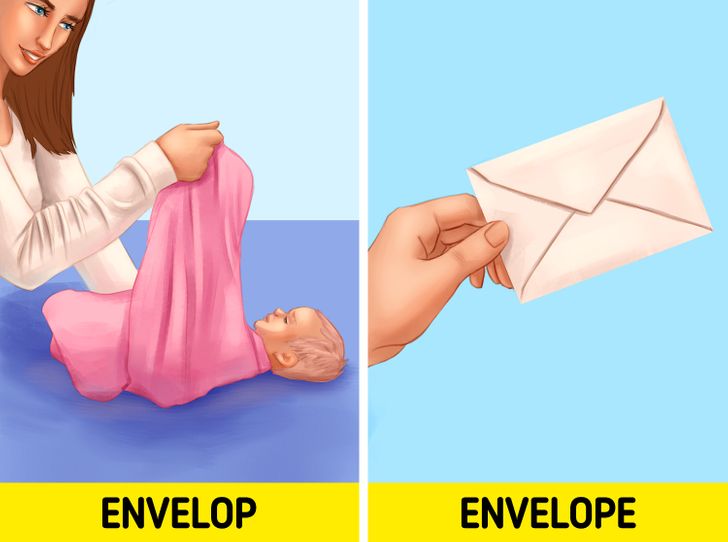
- Envelop (verb): means to enclose, surround, or cover someone or something completely. For example: “We enveloped the baby in Lisa’s jacket because it was very cold outside.”
- Envelope (noun): refers to a paper container used to enclose a card or letter. For example: “He put the birthday card in a yellow envelope and sent it to his sister.”
10. Fair or fare
- Fair (adjective and noun): as an adjective, it refers to a reasonable or just way to treat someone. For example: “He was fair to us after all. We will have to pay the same amount of money.” As a noun, it refers to a large event where people buy and sell goods. For example: “I ran into Paul at the Christmas fair the other day.”
- Fare (noun): refers to the money paid for transportation. For example: “The bus fare is $4 in the afternoon, but it goes up during the evening.”
11. Lie or lay
- Lie (verb): means to rest or recline in a horizontal position over a surface. For example: “I’ll lie down on my bed for a while. I’m exhausted.”
- Lay (verb): means to place something in a flat position for a specific purpose. For example: “Lay your necklace on the table. I want to see if I can fix it.”
12. Lightning or lightening
- Lightning (noun): refers to a flash of light in the sky caused by electricity. For example: “There was a storm with lightning the other day.”
- Lightening (verb): refers to making something lighter or less dark. For example: “He was lightening his mother’s hair on the picture he drew. It was too dark at the beginning.”
13. Lose or loose
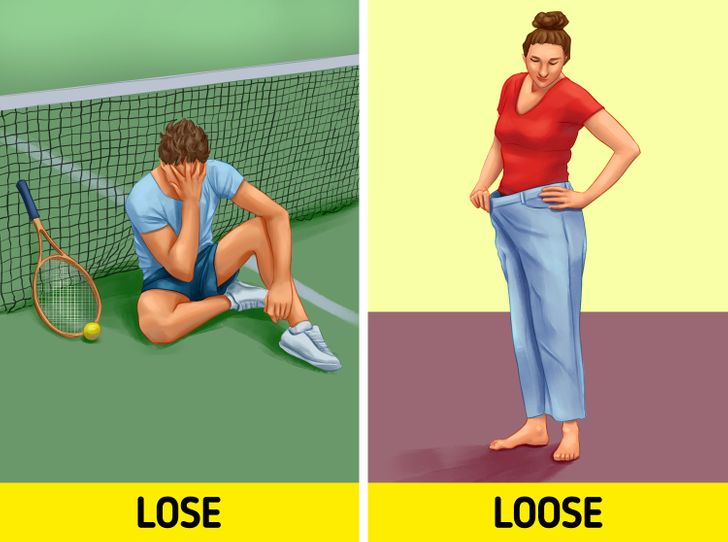

- Lose (verb): means to fail to win something, or to no longer possess something because you cannot find it or do not know where it is. For example: “We lost the match because we didn’t train as much as we should have,” or “I lost my key, so I’ll need to get a copy.”
- Loose (adjective): refers to not being firmly or tightly held, attached, or fastened. For example: “These pants are loose. I need a smaller size.”
14. Personal or personnel
- Personal (adjective): means belonging or relating to a specific person. For example: “We will need your personal information, such as name and address, to register you as a new member.”
- Personnel (noun): refers to the employees of an organization or company. For example: “The director congratulated the personnel for all their achievements.”
15. Raise or rise
16. Stationary or stationery
17. Waist or waste

- Waist (noun): refers to the central part of the body, above the hips and below the upper back or chest. For example: “This dress is too tight around my waist.”
- Waste (noun): refers to the unwanted material left over after something has been used or made. For example: “The construction company had big containers of waste after building these houses.”
18. Wander or wonder
- Wander (verb): means to walk around without having a specific direction or purpose. For example: “She wandered the streets for several minutes before realizing she was lost.”
- Wonder (noun and verb): as a noun, it refers to a feeling of admiration after seeing something amazing or very beautiful. For example: “I stared up at the statue in wonder for 5 minutes.” As a verb, it means to ask questions or express curiosity about something. For example: “I wonder why we didn’t visit any museums when we were in Paris.”
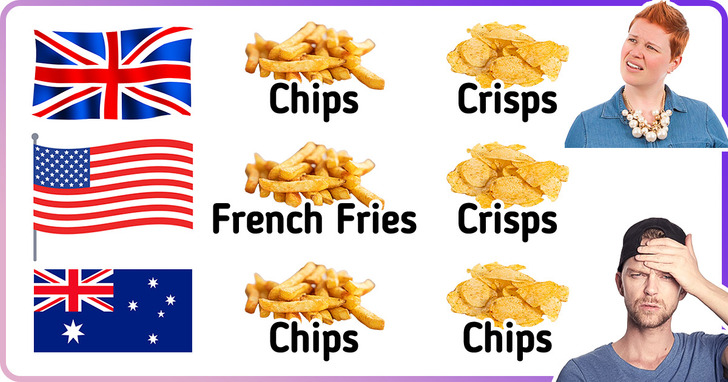
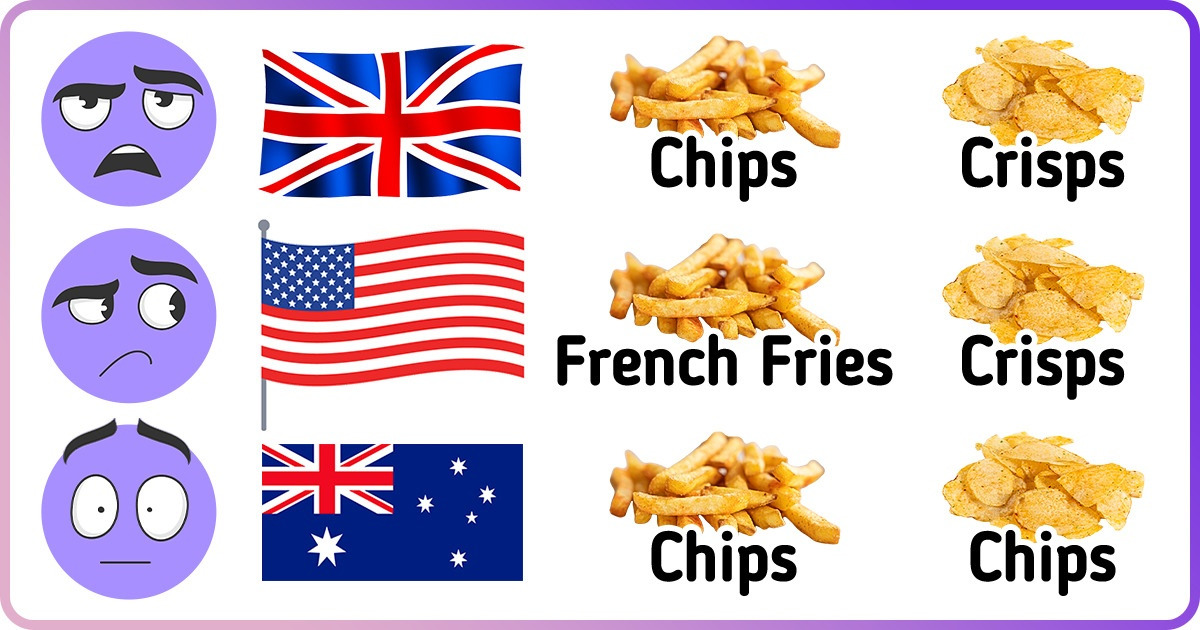
Bonus: French fries, chips, or crisps
We’d love to learn more about the words. Are there any other confusing English words you want to share with us? Please comment below!
Share This Article