A Guide to the Phases of the Moon
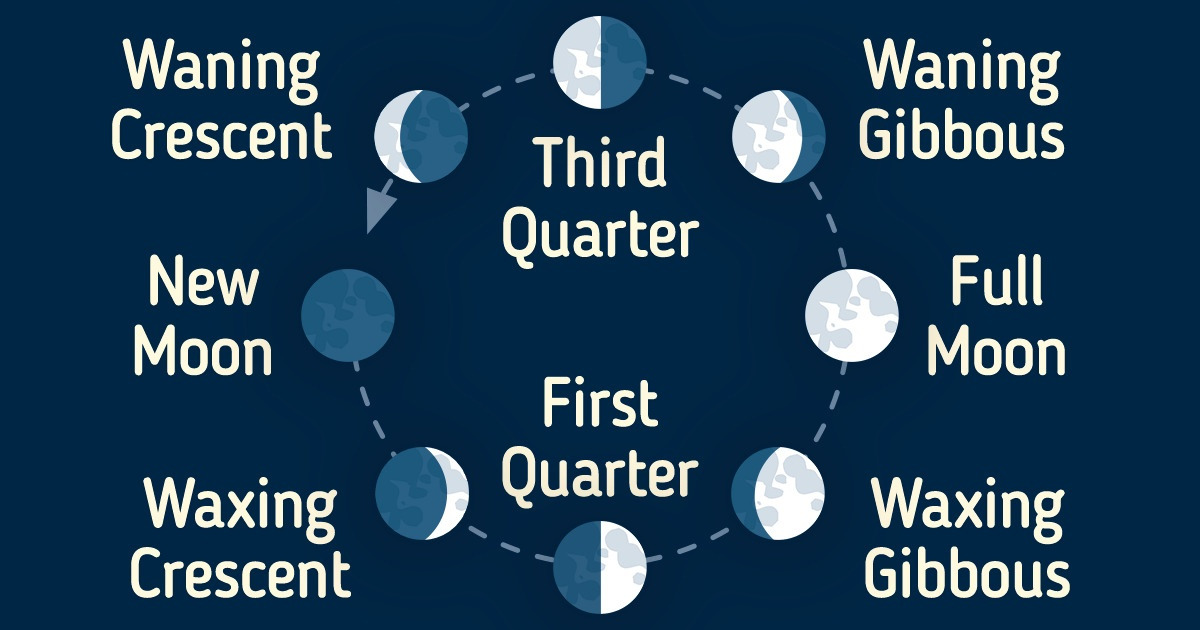
Just like it happens with planet Earth, half of the Moon is illuminated by the Sun, giving it a nightside and a dayside depending on its rotation. In other words, as the Moon travels around the Earth, we will be able to see different sunlit portions of it, which are known as the phases of the Moon.
5-Minute Crafts created this article to show you these 8 phases and their main characteristics when witnessed from the Northern Hemisphere.
💡 Important: Keep in mind that the phases of the Moon are just the same for everyone on Earth. However, if you’re in the Southern Hemisphere, these phases will appear upside down. For instance, while the Waning Crescent appears on the left side when watched from the Northern Hemisphere, the same phase would appear on the right side when seen from the Southern Hemisphere.
1. New Moon
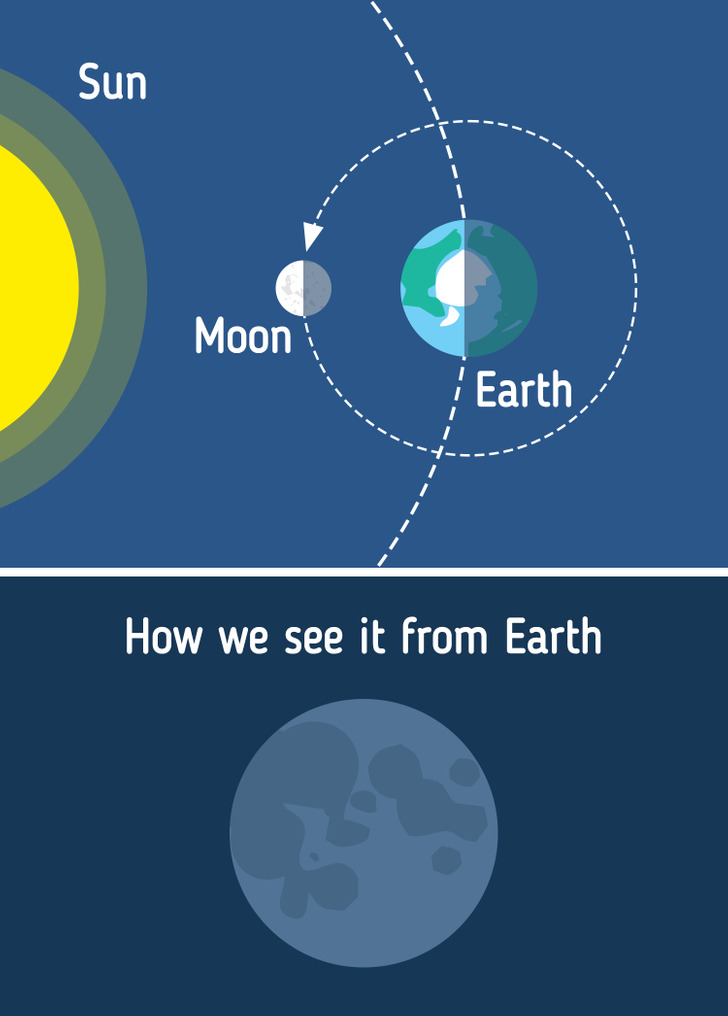
It’s considered the invisible phase as the dark side of the Moon is facing the Earth, and the illuminated side is toward the Sun. That is to say, the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun.
Moreover, the Moon and the Sun are in the same area of the sky, and they both rise and set at the same time.
2. Waxing Crescent

This sliver phase of the Moon happens when the illuminated side looks mostly away from our planet. Therefore, only a very small portion is visible from the Earth.
The Moon grows bigger daily as its orbit moves the Moon’s illuminated side more into view. At the same time, the Moon rises a bit later every day and sets in the afternoon.
3. First Quarter
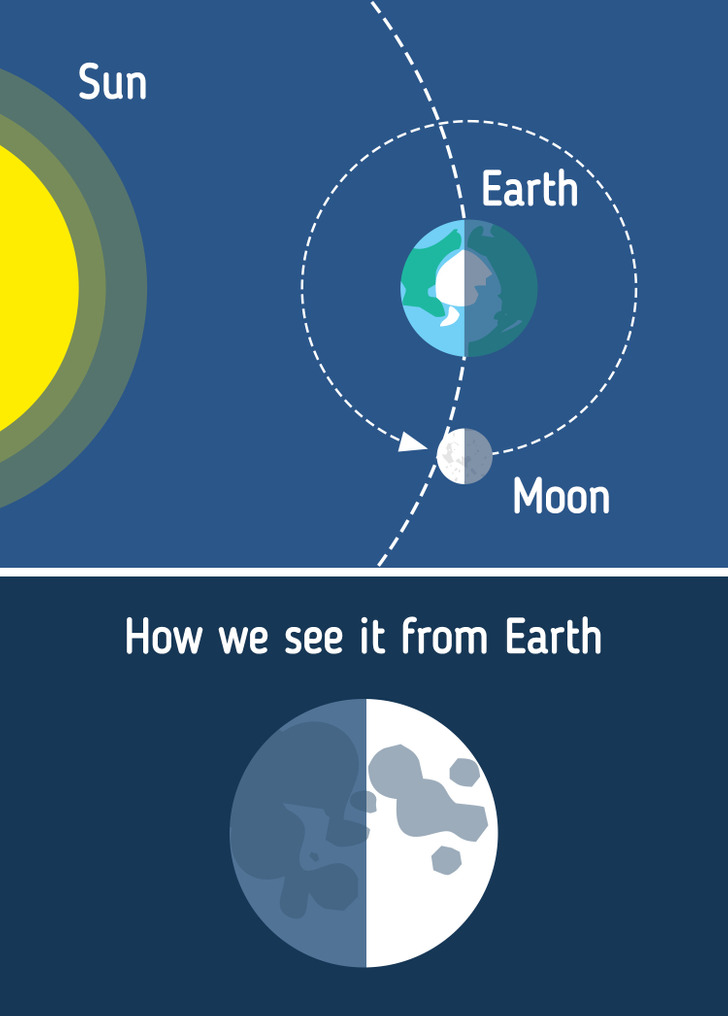
It’s also known as Half Moon as half of the illuminated side is visible. However, that’s not precisely what’s happening with it. What you’re seeing in the sky is just a slice, which means that it’s only a quarter of the entire Moon.
During this phase, the Moon rises around noon, and in the evening you can see it high in the sky to finally observe it set around midnight.
4. Waxing Gibbous

5. Full Moon
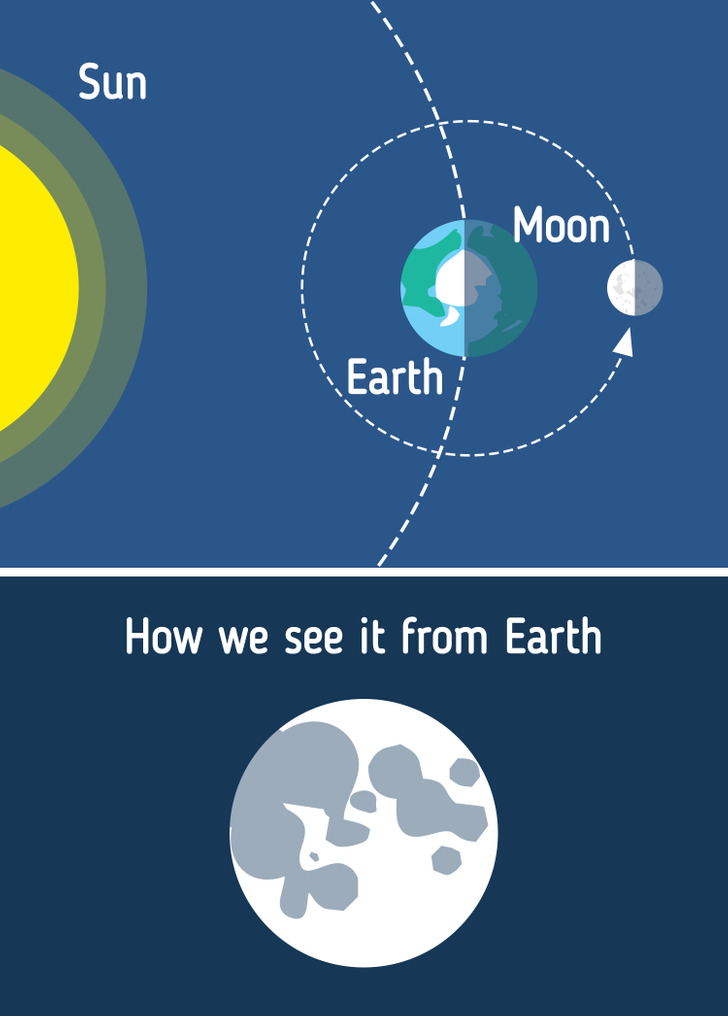
6. Waning Gibbous

The Moon can still be seen quite full some days after the Full Moon phase. However, during the Waning Gibbous phase, the illuminated side seems to narrow down as the Moon’s orbit carries it out from our view and brings it back toward the Sun. Now, the Moon rises in the evening and sets in the morning.
7. Third Quarter
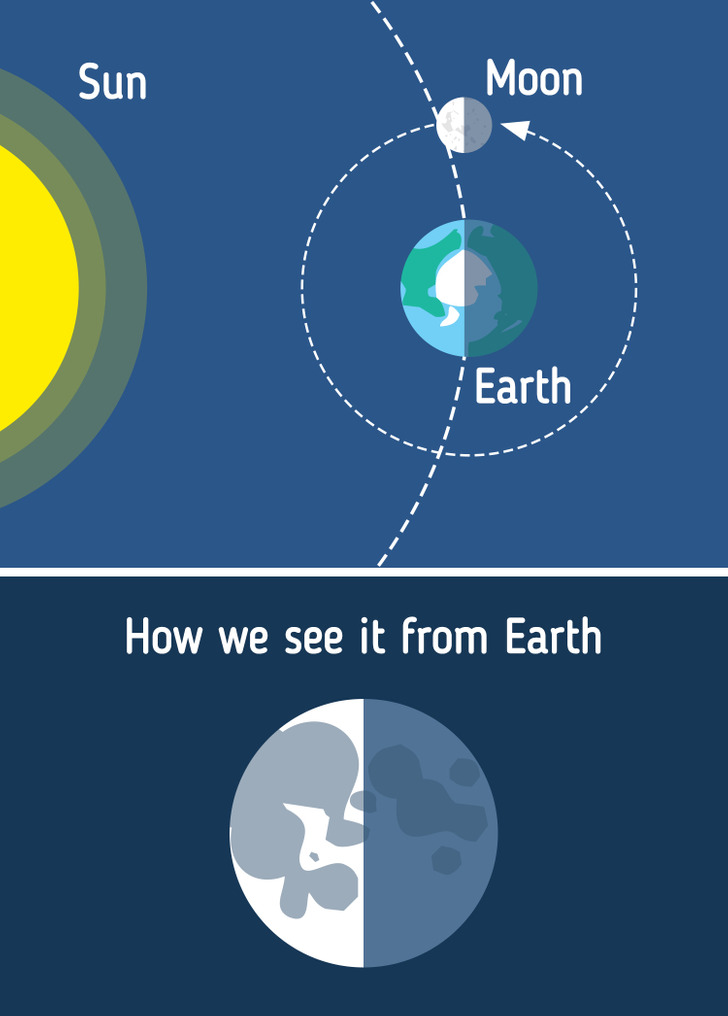
This phase is also known as Last Quarter. Now, the Moon has passed 3-quarters of its orbit around our planet, and seems to be half-illuminated on the left side. However, just like in the First Quarter phase, you’re looking at the half part of the half of the entire Moon. During this phase, the moon rises around midnight and sets around noon.
8. Waning Crescent
