What Satiety Value Is
Why do some dishes make us feel full, while others make us want to visit the fridge in just a short period of time? It turns out that different foods have different satiety values. With this knowledge, you can treat your nutrition more consciously.
5-Minute Crafts would like to tell you about a study that showed how different foods affect our feelings of hunger and satiety.
What satiety value is
Satiety value shows how long a person doesn’t feel hungry after a meal.
The concept of satiety value and satiety index was developed by an Australian researcher and doctor, Susanna Holt.
Foods with high satiety index are often:
- High in appetite inhibitors (potatoes)
- High in protein, which takes longer to digest than other energy sources (meat)
- Low in glycemic index, which takes longer to digest (oats)
- High in fiber, which takes longer to digest than low fiber foods (fruits)
- Low in calories (vegetables)
How the satiety value of different foods was defined

Participants in Susanna Holt’s study ate 240-calorie portions of certain foods every morning, and then they rated their feelings of hunger every 15 minutes. If over the next 2 hours the participants felt hungry, they could go to a buffet table and eat as much as they wanted.
White bread was used as the baseline of 100 during the study. The students rated 38 foods, which were eventually assigned with certain indexes. If the value was more than 100, the food was deemed more satisfying. If the value was less than 100, it was less satisfying.
What the results of the study were
The scientists’ findings can be used in everyday life, especially if you want to start eating less.
- Fatty foods don’t satisfy hunger. This is due to the fact that the body perceives fat as fuel, which should only be used in an emergency. Therefore, it stores it in the cells and doesn’t break it down for instant use. As a result, you continue to feel hungry.
- Carbohydrates raise blood glucose. The body understands that there is enough fuel for work, and the feeling of hunger recedes.
- You can’t say that one food group copes with hunger better than another. For example, not all bakery products are equally effective at satisfying hunger. Croissants, for example, scored the lowest of all foods tested, although most people find them filling.
- The chemical composition of foods matters. For example, beans and lentils contain anti-nutrients that delay their absorption, so you feel full for longer.
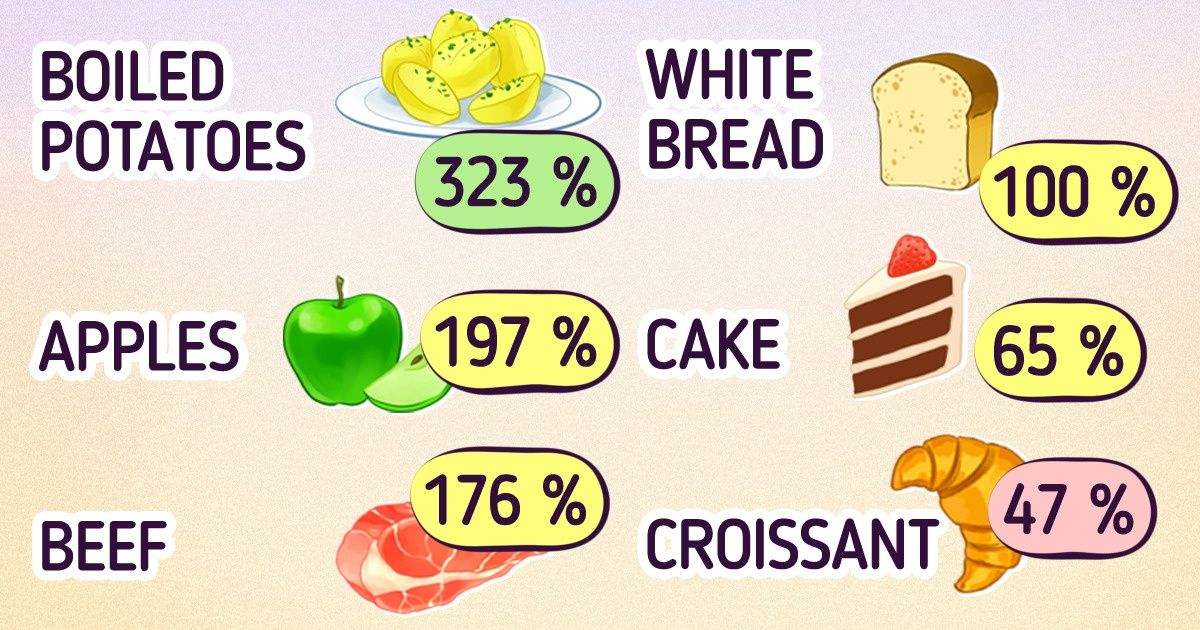
- Boiled potatoes turned out to be the most satisfying.
The satiety index of different foods

- Boiled potatoes — 323%
- Ling fish — 225%
- Oatmeal — 209%
- Oranges — 202%
- Apples — 197%
- Brown pasta — 188%
- Beef — 176%
- Baked beans — 168%
- Grapes — 162%
- Whole meal bread — 157%
- Grain bread — 154%
- Popcorn — 154%
- Eggs — 150%
- Cheese — 146%
- White rice — 138%
- Lentils — 133%
- Brown rice — 132%
- Honeysmacks — 132%
- Crackers — 127%
- Cookies — 120%
- White pasta — 119%
- Bananas — 118%
- Jelly beans — 118%
- Cornflakes — 118%
- French fries — 116%
- White bread — 100%
- Muesli — 100%
- Ice cream — 96%
- Chips — 91%
- Yogurt — 88%
- Peanuts — 84%
- Mars candy bar — 70%
- Doughnuts — 68%
- Cake — 65%
- Croissant — 47%